ArangoDB v3.10 reached End of Life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
This documentation is outdated. Please see the most recent stable version.
Deployments in ArangoGraph
How to create and manage deployments in ArangoGraph
An ArangoGraph deployment is an ArangoDB cluster or single server, configured as you choose.
Each deployment belongs to a project, which belongs to an organization in turn. You can have any number of deployments under one project.
Organizations → Projects → Deployments
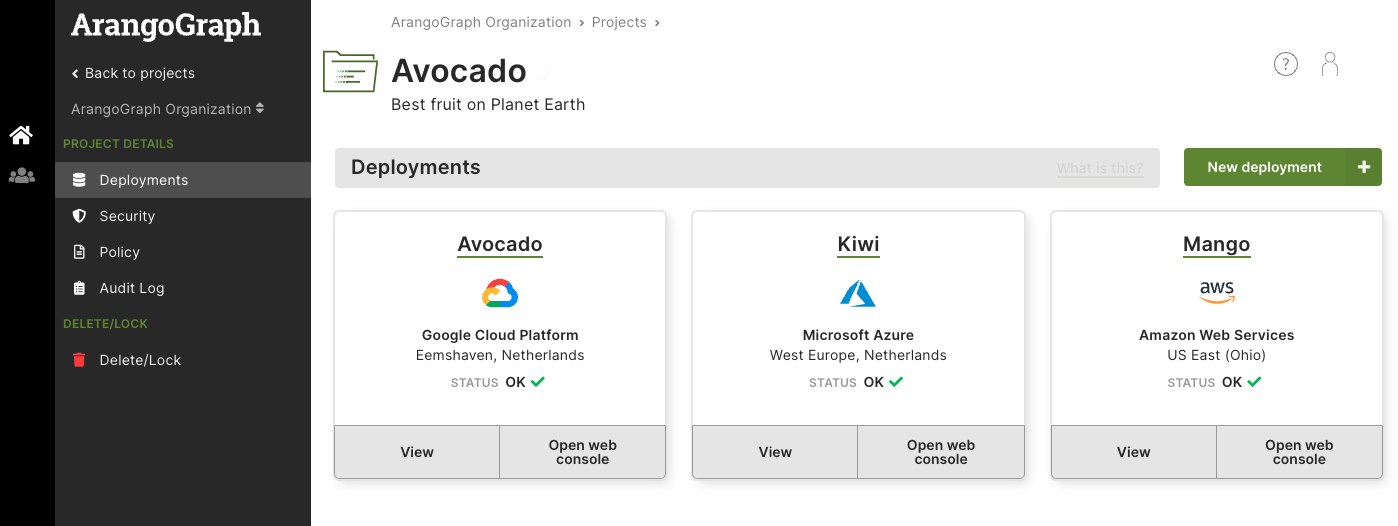
How to create a new deployment
- If you do not have a project yet, create a project first.
- In the main navigation, click Deployments.
- Click the New deployment button.
- Select the project you want to create the deployment for.
- Set up your deployment. The configuration options are described below.
In the General section
- Enter the Name and optionally a Short description for the deployment.
- Select the Provider and Region of the provider.Once a deployment has been created, it is not possible to change the provider and region anymore.
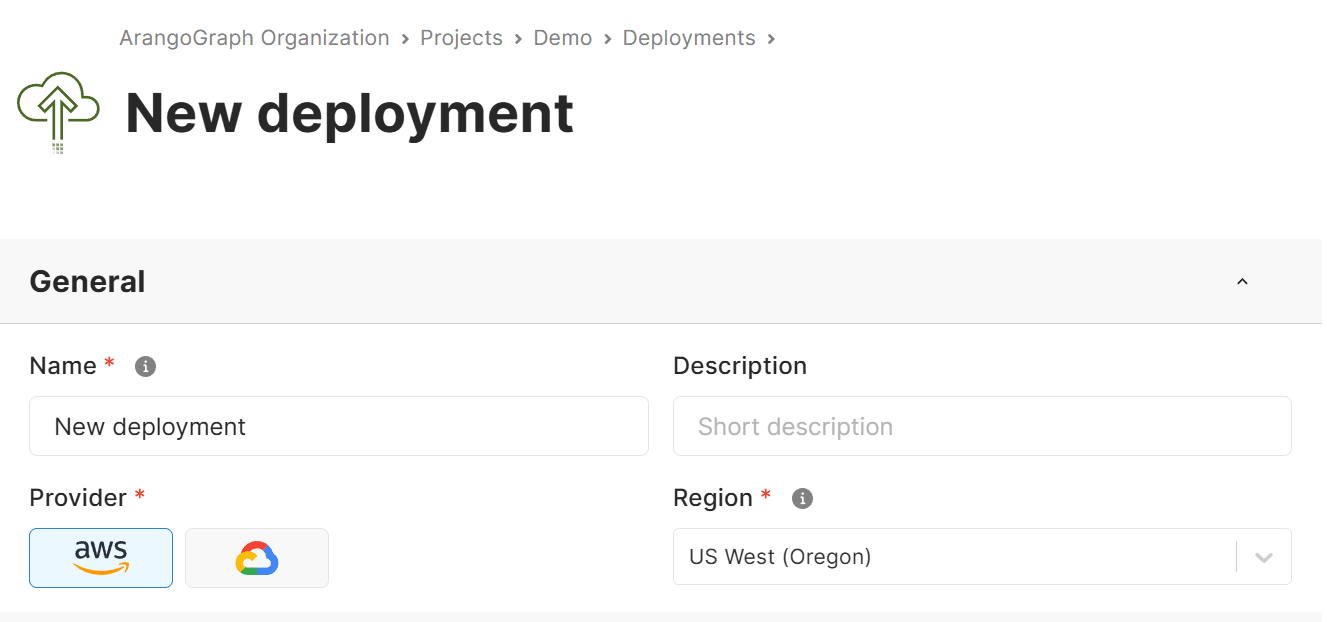
In the Sizing section
Choose a Model for the deployment:
OneShard deployments are suitable when your data set fits in a single node. They are ideal for graph use cases. This model has a fixed number of 3 nodes.
Sharded deployments are suitable when your data set is larger than a single node. The data will be sharded across multiple nodes. You can select the Number of nodes for this deployment model. The more nodes you have, the higher the replication factor can be.
Single Server deployments are suitable when you want to try out ArangoDB without the need for high availability or scalability. The deployment will contain a single server only. Your data will not be replicated and your deployment can be restarted at any time.
Select a NODE SIZE from the list of available options. Each option is a combination of vCPUs, memory, and disk space per node.
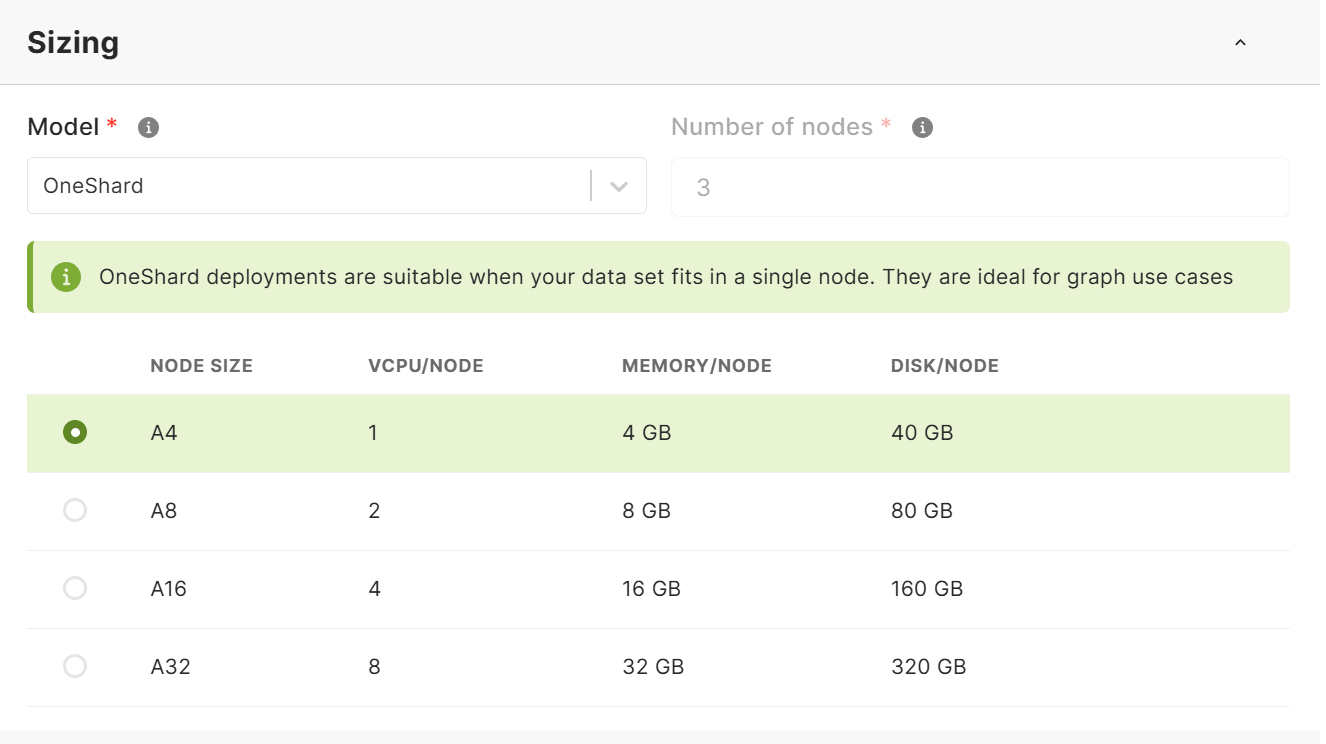
In the Advanced section
- Select the DB Version. If you don’t know which DB version to select, use the version selected by default.
- Select the desired Support Plan. Click the link below the field to get more information about the different support plans.
- In the Certificate field:
- The default certificate created for your project is selected automatically.
- If you have no default certificate, or want to use a new certificate, create a new certificate by typing the desired name for it and hitting enter or clicking Create “<name>” when done.
- Or, if you already have multiple certificates, select the desired one.
- Optional but strongly recommended: In the IP allowlist field, select the
desired one in case you want to limit access to your deployment to certain
IP ranges. To create a allowlist, navigate to your project and select the
IP allowlists tab. See How to manage IP allowlists
for details.For any kind of production deployment it is strongly advise to use an IP allowlist.
- Select a Deployment Profile. Profile options are only available on request.
In the Summary panel
- Review the configuration, and if you’re okay with the setup, press the Create deployment button.
- You are taken to the deployment overview page. Note: Your deployment is being bootstrapped at that point. This process takes a few minutes. Once the deployment is ready, you receive a confirmation email.
How to access your deployment
- In the main navigation, click the Dashboard icon and then click Projects.
- In the Projects page, click the project for which you created a deployment earlier.
- Alternatively, you can access your deployment by clicking Deployments in the dashboard navigation. This page shows all deployments from all projects. Click the name of the deployment you want to view.
- For each deployment in your project, you see the status. While your new deployment is being set up, it displays the bootstrapping status.
- Press the View button to show the deployment page.
- When a deployment displays a status of OK, you can access it.
- Click the Open database UI button or on the database UI link to open the dashboard of your new ArangoDB deployment.
At this point your ArangoDB deployment is available for you to use — Have fun!
If you have disabled the auto-login option to the database web interface, you need to follow the additional steps outlined below to access your deployment:
- Click the copy icon next to the root password. This copies the deployment
root password to your clipboard. You can also click the view icon to unmask
the root password to see it.Do not use the root username/password for everyday operations. It is recommended to use them only to create other user accounts with appropriate permissions.
- Click the Open database UI button or on the database UI link to open the dashboard of your new ArangoDB deployment.
- In the username field type
root, and in the password field paste the password that you copied earlier. - Press the Login button.
- Press the Select DB: _system button.
Each deployment is accessible on two ports:
- Port
8529is the standard port recommended for use by web-browsers. - Port
18529is the alternate port that is recommended for use by automated services.
The difference between these ports is the certificate used. If you enable
Use well-known certificate, the certificates used on port 8529 is well-known
and automatically accepted by most web browsers. The certificate used on port
18529 is a self-signed certificate. For securing automated services, the use of
a self-signed certificate is recommended. Read more on the
Certificates page.
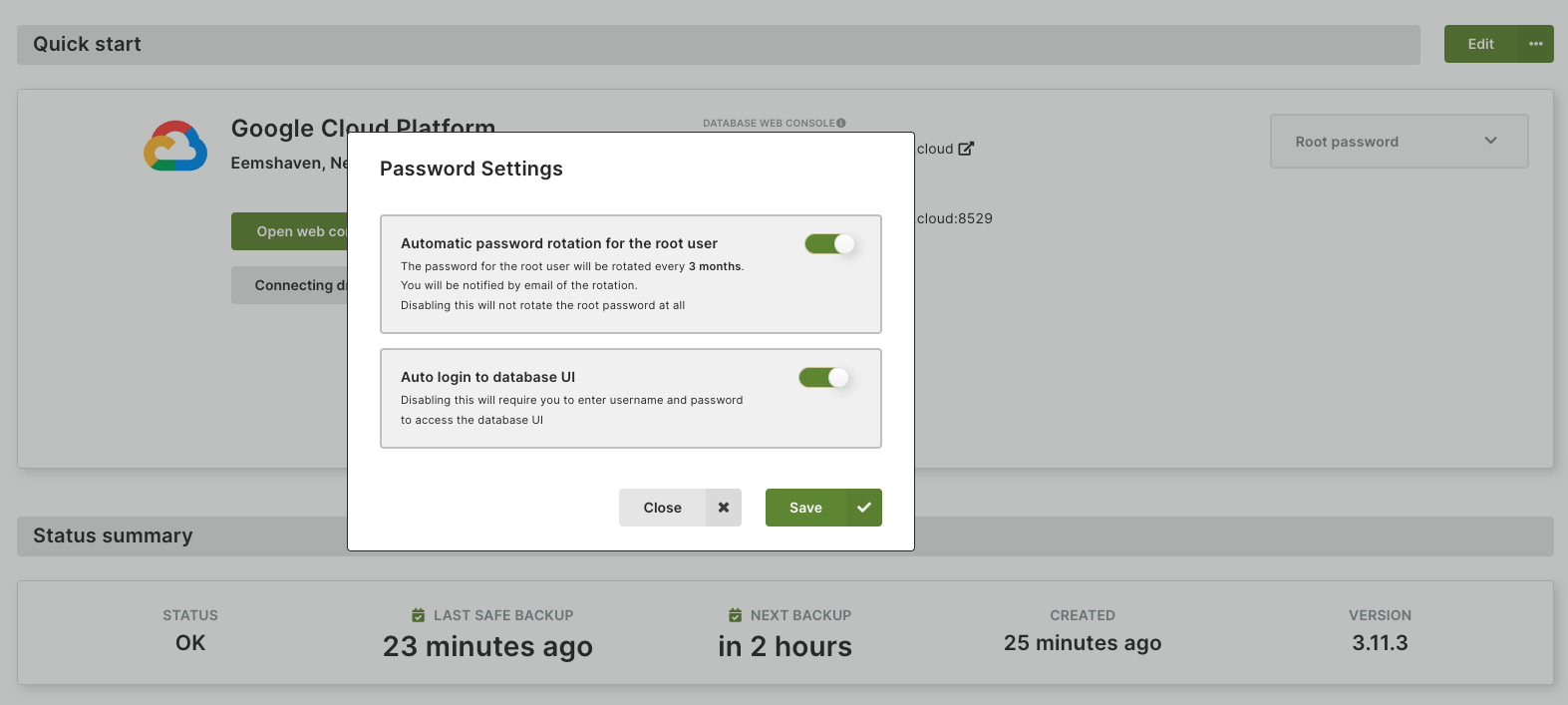
Password settings
How to enable the automatic root user password rotation
Password rotation refers to changing passwords regularly - a security best
practice to reduce the vulnerability to password-based attacks and exploits
by limiting for how long passwords are valid. The ArangoGraph Insights Platform
can automatically change the root user password of an ArangoDB deployment
periodically to improve security.
Navigate to the Deployment for which you want to enable an automatic password rotation for the root user.
In the Quick start section, click the button with the gear icon next to the ROOT PASSWORD.
In the Password Settings dialog, turn the automatic password rotation on and click the Confirm button.
You can expand the Root password panel to see when the password was rotated last. The rotation takes place every three months.
Auto login to database UI
ArangoGraph provides the ability to automatically login to your database using your existing ArangoGraph credentials. This not only provides a seamless experience, preventing you from having to manage multiple sets of credentials but also improves the overall security of your database. As your credentials are shared between ArangoGraph and your database, you can benefit from end-to-end audit traceability for a given user, as well as integration with ArangoGraph SSO.
You can enable this feature in the Password Settings dialog. Please note
that it may take a few minutes to get activated.
Once enabled, you no longer have to fill in the root user and password of
your ArangoDB deployment.
custom DNS setting.This feature can be disabled at any time. You may wish to consider explicitly disabling this feature in the following situations:
- Your workflow requires you to access the database UI using different accounts with differing permission sets, as you cannot switch database users when automatic login is enabled.
- You need to give individuals access to a database’s UI without giving them any access to ArangoGraph. Note, however, that it’s possible to only give an ArangoGraph user database UI access, without other ArangoGraph permissions.
Before getting started, make sure you are signed into ArangoGraph as a user with one of the following permissions in your project:
data.deployment.full-accessdata.deployment.read-only-access
Organization owners have these permissions enabled by default.
The deployment-full-access-user and deployment-read-only-user roles which
contain these permissions can also be granted to other members of the
organization. See how to create a
role binding.
443 port only.How to edit a deployment
You can modify a deployment’s configuration, including the ArangoDB version that is being used, change the memory size, or even switch from a OneShard deployment to a Sharded one if your data set no longer fits in a single node.
- In the main navigation, click Deployments and select an existing deployment from the list, or click Projects, select a project, and then select a deployment.
- In the Quick start section, click the Edit button.
- In the General section, you can do the following:
- Change the deployment name
- Change the deployment description
- In the Sizing section, you can do the following:
- Change OneShard deployments into Sharded deployments. To do so,
select Sharded in the Model dropdown list. You can select the
number of nodes for your deployment. This can also be modified later on.You cannot switch from Sharded back to OneShard.
- Change Single Server deployments into OneShard or Sharded deployments.You cannot switch from Sharded or OneShard back to Single Server.
- Scale up or down the node size.When scaling up or down the size in AWS deployments, the new value gets locked and cannot be changed again until the cloud provider rate limit is reset.
- Change OneShard deployments into Sharded deployments. To do so,
select Sharded in the Model dropdown list. You can select the
number of nodes for your deployment. This can also be modified later on.
- In the Advanced section, you can do the following:
- Upgrade the ArangoDB version that is currently being used. See also Upgrades and Versioning
- Select a different certificate.
- Add or remove an IP allowlist.
- Select a deployment profile.
- All changes are reflected in the Summary panel. Review the new configuration and click Save changes.
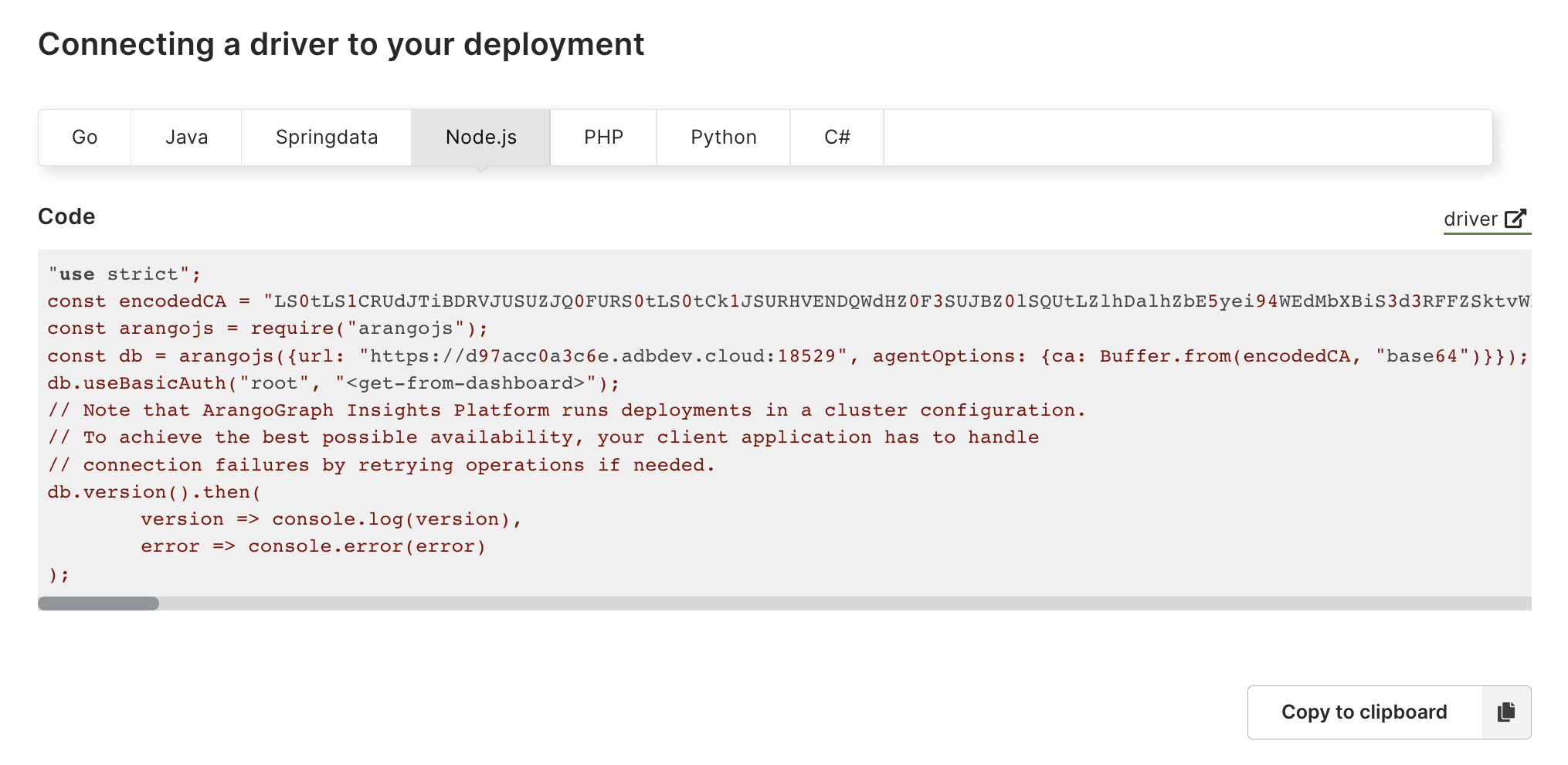
How to connect a driver to your deployment
ArangoDB drivers allow you to use your ArangoGraph deployment as a database system for your applications. Drivers act as interfaces between different programming languages and ArangoDB, which enable you to connect to and manipulate ArangoDB deployments from within compiled programs or using scripting languages.
To get started, open a deployment. In the Quick start section, click on the Connecting drivers button and select your programming language. The code snippets provide examples on how to connect to your instance.
How to delete a deployment
- In the main navigation, in the Projects section, click the project that holds the deployment you wish to delete.
- In the Deployments page, click the deployment you wish to delete.
- Click the Delete/Lock entry in the navigation.
- Click the Delete deployment button.
- In the modal dialog, confirm the deletion by entering
Delete!into the designated text field. - Confirm the deletion by pressing the Yes button.
- You will be taken back to the deployments page of the project. The deployment being deleted will display the Deleting status until it has been successfully removed.
