ArangoDB v3.10 reached End of Life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
This documentation is outdated. Please see the most recent stable version.
ArangoGraphML
Enterprise-ready, graph-powered machine learning as a cloud service or self-managed
Traditional machine learning overlooks the connections and relationships between data points, which is where graph machine learning excels. However, accessibility to GraphML has been limited to sizable enterprises equipped with specialized teams of data scientists. ArangoGraphML, on the other hand, simplifies the utilization of GraphML, enabling a broader range of personas to extract profound insights from their data.
How GraphML works
GraphML focuses on the utilization of neural networks specifically for graph-related tasks. It is well-suited for addressing vague or fuzzy problems and facilitating their resolution. The process involves incorporating a graph’s topology (node and edge structure) and the node and edge characteristics and features to create a numerical representation known as an embedding.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are explicitly designed to learn meaningful numerical representations, or embeddings, for nodes and edges in a graph.
By applying a series of steps, GNNs effectively create graph embeddings, which are numerical representations that encode the essential information about the nodes and edges in the graph. These embeddings can then be used for various tasks, such as node classification, link prediction, and graph-level classification, where the model can make predictions based on the learned patterns and relationships within the graph.
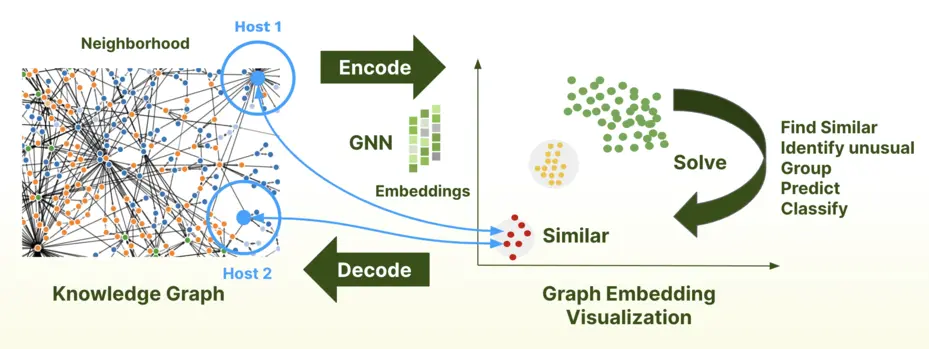
It is no longer necessary to understand the complexities involved with graph machine learning, thanks to the accessibility of the ArangoML package. Solutions with ArangoGraphML only require input from a user about their data, and the ArangoGraphML managed service handles the rest.
The platform comes preloaded with all the tools needed to prepare your graph for machine learning, high-accuracy training, and persisting predictions back to the database for application use.
Classification
Node classification is a natural fit for graph databases as it can leverage existing graph analytics insights during model training. For instance, if you have performed some community detection, potentially using ArangoDB’s built-in Pregel support, you can use these insights as inputs for graph machine learning.
What is Node Classification
The goal of node classification is to categorize the nodes in a graph based on their neighborhood connections and characteristics in the graph. Based on the behaviors or patterns in the graph, the Graph Neural Network (GNN) will be able to learn what makes a node belong to a category.
Node classification can be used to solve complex problems such as:
- Entity Categorization
- Books
- WebPage
- Transaction
- Social Networks
- Events
- Friends
- Interests
- BioPharmaceutical
- Protein-protein interaction
- Drug Categorization
- Sequence grouping
- Behavior
- Fraud
- Purchase/decision making
- Anomaly
Many use cases can be solved with node classification. With many challenges, there are multiple ways to attempt to solve them, and that’s why the ArangoGraphML node classification is only the first of many techniques to be introduced. You can sign up to get immediate access to our latest stable features and also try out other features included in the pipeline, such as embedding similarity or link prediction.
For more information, get in touch with the ArangoDB team.
Metrics and Compliance
Training Performance
Before using a model to provide predictions to your application, there needs to be a way to determine its level of accuracy. Additionally, a mechanism must be in place to ensure the experiments comply with auditor requirements.
ArangoGraphML supports these objectives by storing all relevant training data and metrics in a metadata graph, which is only available to you and is never viewable by ArangoDB. This metagraph contains valuable training metrics such as average accuracy (the general metric for determining model performance), F1, Recall, Precision, and confusion matrix data. This graph links all experiments to the source data, feature generation activities, training runs, and prediction jobs. Having everything linked across the entire pipeline ensures that, at any time, anything done that could be considered associated with sensitive user data, it is logged and easily accessible.
Security
Each deployment that uses ArangoGraphML has an arangopipe database created,
which houses all this information. Since the data lives with the deployment,
it benefits from the ArangoGraph SOC 2 compliance and Enterprise security features.
All ArangoGraphML services live alongside the ArangoGraph deployment and are only
accessible within that organization.
