ArangoDB v3.10 reached End of Life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
This documentation is outdated. Please see the most recent stable version.
HTTP API Documentation
All functionality of ArangoDB servers is provided via a RESTful API over the HTTP protocol, and you can call the API endpoints directly, via database drivers, or other tools
ArangoDB servers expose an application programming interface (API) for managing the database system. It is based on the HTTP protocol that powers the world wide web. All interactions with a server are ultimately carried out via this HTTP API.
You can use the API by sending HTTP requests to the server directly, but the more common way of communicating with the server is via a database driver. A driver abstracts the complexity of the API away by providing a simple interface for your programming language or environment and handling things like authentication, connection pooling, asynchronous requests, and multi-part replies in the background. You can also use ArangoDB’s web interface, the arangosh shell, or other tools.
The API documentation is relevant for you in the following cases:
- You want to build or extend a driver.
- You want to utilize a feature that isn’t exposed by your driver or tool.
- You need to send many requests and avoid any overhead that a driver or tool might add.
- You operate a server instance and need to perform administrative actions via the API.
- You are interested in how the low-level communication works.
RESTful API
The API adheres to the design principles of REST
(Representational State Transfer). A REST API is a specific type of HTTP API
that uses HTTP methods to represent operations on resources (mainly GET,
POST, PATCH, PUT, and DELETE), and resources are identified by URIs.
A resource can be a database record, a server log, or any other data entity or
object. The communication between client and server is stateless.
A request URL can look like this:
http://localhost:8529/_db/DATABASE/_api/document/COLLECTION/KEY?returnOld=true&keepNull=false
httpis the scheme, which ishttpsif you use TLS encryptionhttp:is the protocollocalhostis the hostname, which can be an IP address or domain name including subdomains8529is the port/_db/DATABASE/_api/document/COLLECTION/KEYis the pathname?returnOld=true&keepNull=falseis the search stringreturnOld=true&keepNull=falseis the query string
The HTTP API documentation mainly describes the available endpoints, like
for updating a document, creating a graph, and so on. Each endpoint description
starts with the HTTP method and the pathname, like PATCH /_api/document/{collection}/{key}.
- The
PATCHmethod is for updating,PUTfor replacing,POSTfor creating (or triggering an action),DELETEfor removing,GETfor reading,HEADfor reading metadata only /_api/document/…is the path of ArangoDB’s HTTP API for handling documents and can be preceded by/_db/{database}with{database}replaced by a database name to select another database than the default_systemdatabase{collection}and{key}are placeholders called Path Parameters that you have to replace with a collection name and document key in this case- The pathname can be followed by a question mark and the so-called
Query Parameters, which is a series of key/value pairs separated by
ampersands to set options, like
/_api/document/COLLECTION/KEY?returnOld=true&keepNull=false - Some endpoints allow you to specify HTTP headers in the request
(not in the URL), like
If-Match: "REVISION" - A Request Body is the payload you may need to send, typically JSON data
- Responses are the possible HTTP responses in reply to your request in terms of the HTTP status code and typically a JSON payload with a result or error information
On the wire, a simplified HTTP request can look like this:
PATCH /_api/document/coll1/docA?returnOld=true HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8529
Authorization: Basic cm9vdDo=
If-Match: "_hV2oH9y---"
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 20
{"attr":"new value"}
And a simplified HTTP response can look like this:
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted
Etag: "_hV2r5XW---"
Location: /_db/_system/_api/document/coll1/docA
Server: ArangoDB
Connection: Keep-Alive
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 160
{"_id":"coll1/docA","_key":"docA","_rev":"_hV2r5XW---","_oldRev":"_hV2oH9y---","old":{"_key":"docA","_id":"coll1/docA","_rev":"_hV2oH9y---","attr":"value"}}
Swagger specification
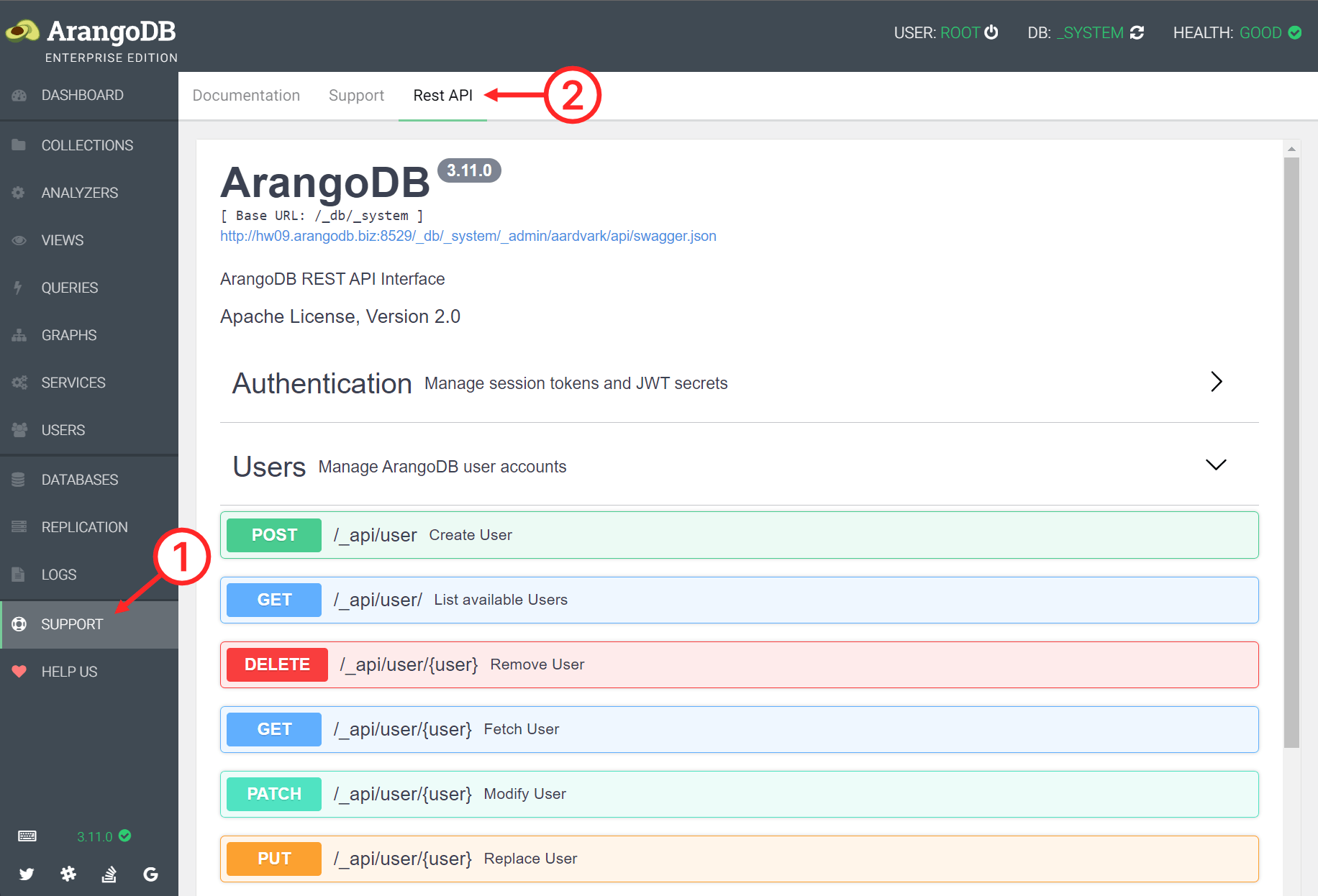
ArangoDB’s RESTful HTTP API is documented using the industry-standard OpenAPI Specification, more specifically OpenAPI version 3.1 . You can explore the API with the interactive Swagger UI using the ArangoDB web interface.
- Click SUPPORT in the main navigation of the web interface.
- Click the Rest API tab.
- Click a section and endpoint to view the description and parameters.
Also see this blog post: Using the ArangoDB Swagger.io Interactive API Documentation .
