ArangoDB v3.10 reached End of Life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
This documentation is outdated. Please see the most recent stable version.
Example graphs
How to use the example graphs built into ArangoDB
ArangoDB comes with a set of easy-to-understand graphs for demonstration purposes.
In the web interface, navigate to the GRAPHS section, click the Add Graph card, go to the Examples tab, and click the Create button of one of the listed graphs.
In arangosh, run
require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph").loadGraph("<name>");with<name>substituted by the name of an example graph listed below.
You can visually explore the created graphs in the Graph viewer of the web interface.
You can take a look at the script that creates the example graphs on GitHub for reference about how to manage graphs programmatically.
Knows Graph
The knows graph is a set of persons knowing each other:
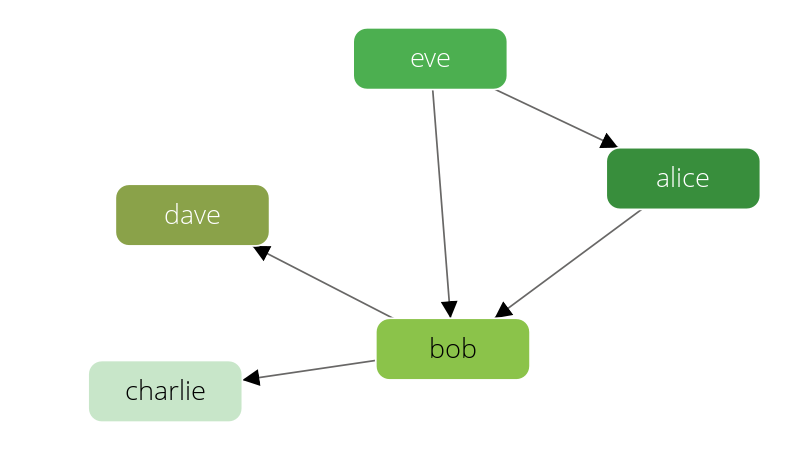
The graph consists of a persons vertex collection connected via a knows
edge collection.
There are five persons, Alice, Bob, Charlie, Dave, and Eve.
They have the following directed relations:
- Alice knows Bob
- Bob knows Charlie
- Bob knows Dave
- Eve knows Alice
- Eve knows Bob
Example of how to create the graph, inspect its vertices and edges, and delete it again:
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var g = examples.loadGraph("knows_graph");
db.persons.toArray()
db.knows.toArray();
examples.dropGraph("knows_graph");Show output
[
{
"_key" : "alice",
"_id" : "persons/alice",
"_rev" : "_holfoDu---",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_key" : "bob",
"_id" : "persons/bob",
"_rev" : "_holfoDy---",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_key" : "charlie",
"_id" : "persons/charlie",
"_rev" : "_holfoDy--_",
"name" : "Charlie"
},
{
"_key" : "dave",
"_id" : "persons/dave",
"_rev" : "_holfoDy--A",
"name" : "Dave"
},
{
"_key" : "eve",
"_id" : "persons/eve",
"_rev" : "_holfoDy--B",
"name" : "Eve"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "72293",
"_id" : "knows/72293",
"_from" : "persons/alice",
"_to" : "persons/bob",
"_rev" : "_holfoDy--C",
"vertex" : "alice"
},
{
"_key" : "72295",
"_id" : "knows/72295",
"_from" : "persons/bob",
"_to" : "persons/charlie",
"_rev" : "_holfoDy--D",
"vertex" : "bob"
},
{
"_key" : "72297",
"_id" : "knows/72297",
"_from" : "persons/bob",
"_to" : "persons/dave",
"_rev" : "_holfoDy--E",
"vertex" : "bob"
},
{
"_key" : "72299",
"_id" : "knows/72299",
"_from" : "persons/eve",
"_to" : "persons/alice",
"_rev" : "_holfoD2---",
"vertex" : "eve"
},
{
"_key" : "72301",
"_id" : "knows/72301",
"_from" : "persons/eve",
"_to" : "persons/bob",
"_rev" : "_holfoD2--_",
"vertex" : "eve"
}
]Note: With the default traversal depth of 2 of the graph viewer, you may not see all edges of this graph by default.
Traversal Graph
The traversalGraph has been designed to demonstrate filters in traversals.
It has some labels to filter on it. The graph’s vertices are in a collection
called circles, and it has an edge collection edges to connect them.
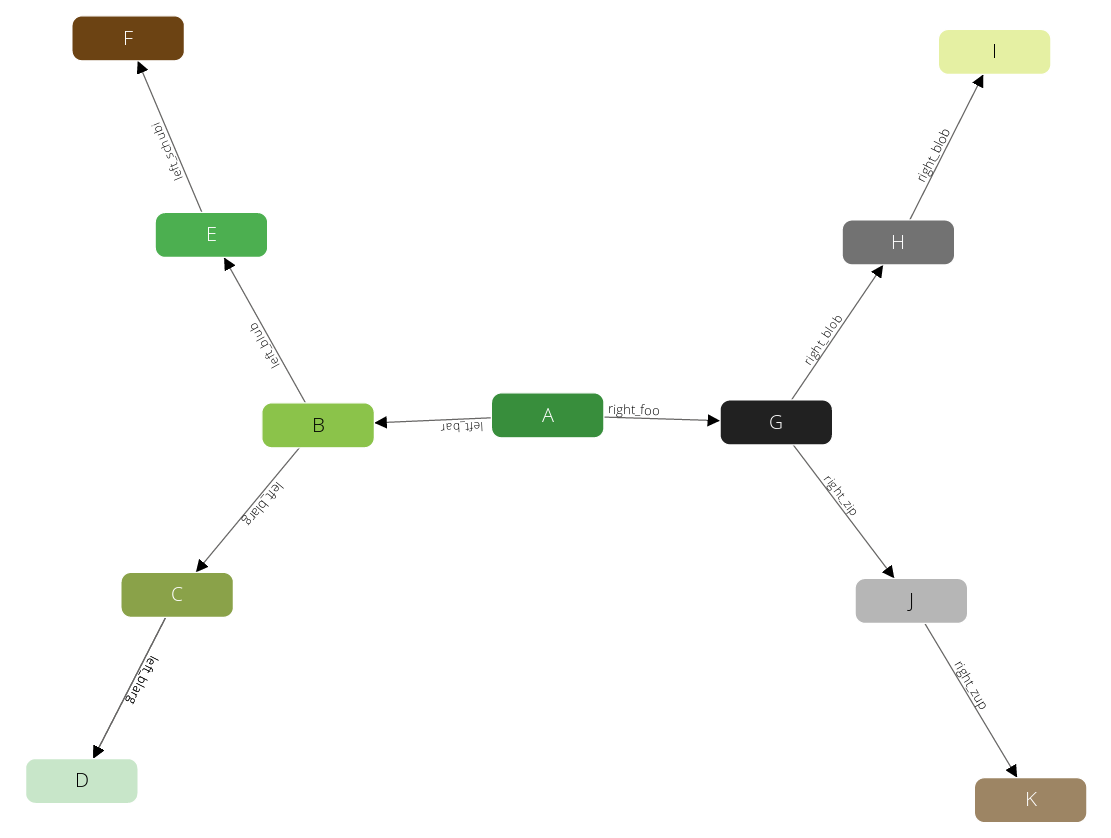
Circles have unique numeric labels. Edges have two boolean attributes
(theFalse always being false, theTruth always being true) and a label
sorting B - D to the left side, G - K to the right side.
Left and right side split into paths - at B and G, which are each direct
neighbors of the root-node A. Starting from A, the graph has a depth of 3 on
all its paths.
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var g = examples.loadGraph("traversalGraph");
db.circles.toArray();
db.edges.toArray();
examples.dropGraph("traversalGraph");Show output
[
{
"_key" : "A",
"_id" : "circles/A",
"_rev" : "_holfoEe---",
"label" : "1"
},
{
"_key" : "B",
"_id" : "circles/B",
"_rev" : "_holfoEe--_",
"label" : "2"
},
{
"_key" : "C",
"_id" : "circles/C",
"_rev" : "_holfoEi---",
"label" : "3"
},
{
"_key" : "D",
"_id" : "circles/D",
"_rev" : "_holfoEi--_",
"label" : "4"
},
{
"_key" : "E",
"_id" : "circles/E",
"_rev" : "_holfoEi--A",
"label" : "5"
},
{
"_key" : "F",
"_id" : "circles/F",
"_rev" : "_holfoEi--B",
"label" : "6"
},
{
"_key" : "G",
"_id" : "circles/G",
"_rev" : "_holfoEm---",
"label" : "7"
},
{
"_key" : "H",
"_id" : "circles/H",
"_rev" : "_holfoEm--_",
"label" : "8"
},
{
"_key" : "I",
"_id" : "circles/I",
"_rev" : "_holfoEm--A",
"label" : "9"
},
{
"_key" : "J",
"_id" : "circles/J",
"_rev" : "_holfoEm--B",
"label" : "10"
},
{
"_key" : "K",
"_id" : "circles/K",
"_rev" : "_holfoEm--C",
"label" : "11"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "72354",
"_id" : "edges/72354",
"_from" : "circles/A",
"_to" : "circles/B",
"_rev" : "_holfoEm--D",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_bar"
},
{
"_key" : "72356",
"_id" : "edges/72356",
"_from" : "circles/B",
"_to" : "circles/C",
"_rev" : "_holfoEq---",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_blarg"
},
{
"_key" : "72358",
"_id" : "edges/72358",
"_from" : "circles/C",
"_to" : "circles/D",
"_rev" : "_holfoEq--_",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_blorg"
},
{
"_key" : "72360",
"_id" : "edges/72360",
"_from" : "circles/B",
"_to" : "circles/E",
"_rev" : "_holfoEq--A",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_blub"
},
{
"_key" : "72362",
"_id" : "edges/72362",
"_from" : "circles/E",
"_to" : "circles/F",
"_rev" : "_holfoEq--B",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_schubi"
},
{
"_key" : "72364",
"_id" : "edges/72364",
"_from" : "circles/A",
"_to" : "circles/G",
"_rev" : "_holfoEq--C",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_foo"
},
{
"_key" : "72366",
"_id" : "edges/72366",
"_from" : "circles/G",
"_to" : "circles/H",
"_rev" : "_holfoEu---",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_blob"
},
{
"_key" : "72368",
"_id" : "edges/72368",
"_from" : "circles/H",
"_to" : "circles/I",
"_rev" : "_holfoEu--_",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_blub"
},
{
"_key" : "72370",
"_id" : "edges/72370",
"_from" : "circles/G",
"_to" : "circles/J",
"_rev" : "_holfoEu--A",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_zip"
},
{
"_key" : "72372",
"_id" : "edges/72372",
"_from" : "circles/J",
"_to" : "circles/K",
"_rev" : "_holfoEu--B",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_zup"
}
]Note: With the default traversal depth of 2 of the graph viewer, you may not see all edges of this graph by default.
k Shortest Paths Graph
The vertices in the kShortestPathsGraph graph are train stations of cities in
Europe and North America. The edges represent train connections between them,
with the travel time for both directions as edge weight.
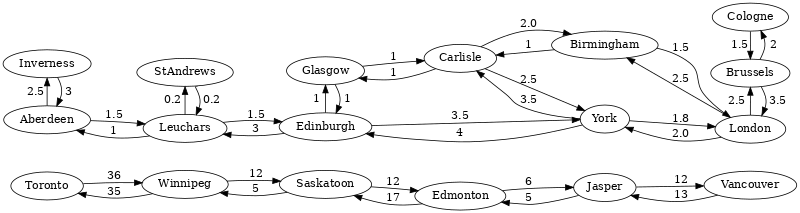
See the k Shortest Paths page for query examples.
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var g = examples.loadGraph("kShortestPathsGraph");
db.places.toArray();
db.connections.toArray();
examples.dropGraph("kShortestPathsGraph");Show output
[
{
"_key" : "Inverness",
"_id" : "places/Inverness",
"_rev" : "_holfoGS---",
"label" : "Inverness"
},
{
"_key" : "Aberdeen",
"_id" : "places/Aberdeen",
"_rev" : "_holfoGS--_",
"label" : "Aberdeen"
},
{
"_key" : "Leuchars",
"_id" : "places/Leuchars",
"_rev" : "_holfoGS--A",
"label" : "Leuchars"
},
{
"_key" : "StAndrews",
"_id" : "places/StAndrews",
"_rev" : "_holfoGW---",
"label" : "StAndrews"
},
{
"_key" : "Edinburgh",
"_id" : "places/Edinburgh",
"_rev" : "_holfoGW--_",
"label" : "Edinburgh"
},
{
"_key" : "Glasgow",
"_id" : "places/Glasgow",
"_rev" : "_holfoGW--A",
"label" : "Glasgow"
},
{
"_key" : "York",
"_id" : "places/York",
"_rev" : "_holfoGW--B",
"label" : "York"
},
{
"_key" : "Carlisle",
"_id" : "places/Carlisle",
"_rev" : "_holfoGW--C",
"label" : "Carlisle"
},
{
"_key" : "Birmingham",
"_id" : "places/Birmingham",
"_rev" : "_holfoGW--D",
"label" : "Birmingham"
},
{
"_key" : "London",
"_id" : "places/London",
"_rev" : "_holfoGa---",
"label" : "London"
},
{
"_key" : "Brussels",
"_id" : "places/Brussels",
"_rev" : "_holfoGa--_",
"label" : "Brussels"
},
{
"_key" : "Cologne",
"_id" : "places/Cologne",
"_rev" : "_holfoGa--A",
"label" : "Cologne"
},
{
"_key" : "Toronto",
"_id" : "places/Toronto",
"_rev" : "_holfoGa--B",
"label" : "Toronto"
},
{
"_key" : "Winnipeg",
"_id" : "places/Winnipeg",
"_rev" : "_holfoGa--C",
"label" : "Winnipeg"
},
{
"_key" : "Saskatoon",
"_id" : "places/Saskatoon",
"_rev" : "_holfoGe---",
"label" : "Saskatoon"
},
{
"_key" : "Edmonton",
"_id" : "places/Edmonton",
"_rev" : "_holfoGe--_",
"label" : "Edmonton"
},
{
"_key" : "Jasper",
"_id" : "places/Jasper",
"_rev" : "_holfoGe--A",
"label" : "Jasper"
},
{
"_key" : "Vancouver",
"_id" : "places/Vancouver",
"_rev" : "_holfoGe--B",
"label" : "Vancouver"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "72432",
"_id" : "connections/72432",
"_from" : "places/Inverness",
"_to" : "places/Aberdeen",
"_rev" : "_holfoGe--C",
"travelTime" : 3
},
{
"_key" : "72434",
"_id" : "connections/72434",
"_from" : "places/Aberdeen",
"_to" : "places/Inverness",
"_rev" : "_holfoGe--D",
"travelTime" : 2.5
},
{
"_key" : "72436",
"_id" : "connections/72436",
"_from" : "places/Aberdeen",
"_to" : "places/Leuchars",
"_rev" : "_holfoGi---",
"travelTime" : 1.5
},
{
"_key" : "72438",
"_id" : "connections/72438",
"_from" : "places/Leuchars",
"_to" : "places/Aberdeen",
"_rev" : "_holfoGi--_",
"travelTime" : 1
},
{
"_key" : "72440",
"_id" : "connections/72440",
"_from" : "places/Leuchars",
"_to" : "places/Edinburgh",
"_rev" : "_holfoGi--A",
"travelTime" : 1.5
},
{
"_key" : "72442",
"_id" : "connections/72442",
"_from" : "places/Edinburgh",
"_to" : "places/Leuchars",
"_rev" : "_holfoGi--B",
"travelTime" : 3
},
{
"_key" : "72444",
"_id" : "connections/72444",
"_from" : "places/Edinburgh",
"_to" : "places/Glasgow",
"_rev" : "_holfoGi--C",
"travelTime" : 1
},
{
"_key" : "72446",
"_id" : "connections/72446",
"_from" : "places/Glasgow",
"_to" : "places/Edinburgh",
"_rev" : "_holfoGi--D",
"travelTime" : 1
},
{
"_key" : "72448",
"_id" : "connections/72448",
"_from" : "places/Edinburgh",
"_to" : "places/York",
"_rev" : "_holfoGm---",
"travelTime" : 3.5
},
{
"_key" : "72450",
"_id" : "connections/72450",
"_from" : "places/York",
"_to" : "places/Edinburgh",
"_rev" : "_holfoGm--_",
"travelTime" : 4
},
{
"_key" : "72452",
"_id" : "connections/72452",
"_from" : "places/Glasgow",
"_to" : "places/Carlisle",
"_rev" : "_holfoGm--A",
"travelTime" : 1
},
{
"_key" : "72454",
"_id" : "connections/72454",
"_from" : "places/Carlisle",
"_to" : "places/Glasgow",
"_rev" : "_holfoGm--B",
"travelTime" : 1
},
{
"_key" : "72456",
"_id" : "connections/72456",
"_from" : "places/Carlisle",
"_to" : "places/York",
"_rev" : "_holfoGm--C",
"travelTime" : 2.5
},
{
"_key" : "72458",
"_id" : "connections/72458",
"_from" : "places/York",
"_to" : "places/Carlisle",
"_rev" : "_holfoGm--D",
"travelTime" : 3.5
},
{
"_key" : "72460",
"_id" : "connections/72460",
"_from" : "places/Carlisle",
"_to" : "places/Birmingham",
"_rev" : "_holfoGq---",
"travelTime" : 2
},
{
"_key" : "72462",
"_id" : "connections/72462",
"_from" : "places/Birmingham",
"_to" : "places/Carlisle",
"_rev" : "_holfoGq--_",
"travelTime" : 1
},
{
"_key" : "72464",
"_id" : "connections/72464",
"_from" : "places/Birmingham",
"_to" : "places/London",
"_rev" : "_holfoGq--A",
"travelTime" : 1.5
},
{
"_key" : "72466",
"_id" : "connections/72466",
"_from" : "places/London",
"_to" : "places/Birmingham",
"_rev" : "_holfoGq--B",
"travelTime" : 2.5
},
{
"_key" : "72468",
"_id" : "connections/72468",
"_from" : "places/Leuchars",
"_to" : "places/StAndrews",
"_rev" : "_holfoGu---",
"travelTime" : 0.2
},
{
"_key" : "72470",
"_id" : "connections/72470",
"_from" : "places/StAndrews",
"_to" : "places/Leuchars",
"_rev" : "_holfoGu--_",
"travelTime" : 0.2
},
{
"_key" : "72472",
"_id" : "connections/72472",
"_from" : "places/York",
"_to" : "places/London",
"_rev" : "_holfoGu--A",
"travelTime" : 1.8
},
{
"_key" : "72474",
"_id" : "connections/72474",
"_from" : "places/London",
"_to" : "places/York",
"_rev" : "_holfoGu--B",
"travelTime" : 2
},
{
"_key" : "72476",
"_id" : "connections/72476",
"_from" : "places/London",
"_to" : "places/Brussels",
"_rev" : "_holfoGy---",
"travelTime" : 2.5
},
{
"_key" : "72478",
"_id" : "connections/72478",
"_from" : "places/Brussels",
"_to" : "places/London",
"_rev" : "_holfoGy--_",
"travelTime" : 3.5
},
{
"_key" : "72480",
"_id" : "connections/72480",
"_from" : "places/Brussels",
"_to" : "places/Cologne",
"_rev" : "_holfoGy--A",
"travelTime" : 2
},
{
"_key" : "72482",
"_id" : "connections/72482",
"_from" : "places/Cologne",
"_to" : "places/Brussels",
"_rev" : "_holfoGy--B",
"travelTime" : 1.5
},
{
"_key" : "72484",
"_id" : "connections/72484",
"_from" : "places/Toronto",
"_to" : "places/Winnipeg",
"_rev" : "_holfoGy--C",
"travelTime" : 36
},
{
"_key" : "72486",
"_id" : "connections/72486",
"_from" : "places/Winnipeg",
"_to" : "places/Toronto",
"_rev" : "_holfoGy--D",
"travelTime" : 35
},
{
"_key" : "72488",
"_id" : "connections/72488",
"_from" : "places/Winnipeg",
"_to" : "places/Saskatoon",
"_rev" : "_holfoG2---",
"travelTime" : 12
},
{
"_key" : "72490",
"_id" : "connections/72490",
"_from" : "places/Saskatoon",
"_to" : "places/Winnipeg",
"_rev" : "_holfoG2--_",
"travelTime" : 5
},
{
"_key" : "72492",
"_id" : "connections/72492",
"_from" : "places/Saskatoon",
"_to" : "places/Edmonton",
"_rev" : "_holfoG2--A",
"travelTime" : 12
},
{
"_key" : "72494",
"_id" : "connections/72494",
"_from" : "places/Edmonton",
"_to" : "places/Saskatoon",
"_rev" : "_holfoG2--B",
"travelTime" : 17
},
{
"_key" : "72496",
"_id" : "connections/72496",
"_from" : "places/Edmonton",
"_to" : "places/Jasper",
"_rev" : "_holfoG6---",
"travelTime" : 6
},
{
"_key" : "72498",
"_id" : "connections/72498",
"_from" : "places/Jasper",
"_to" : "places/Edmonton",
"_rev" : "_holfoG6--_",
"travelTime" : 5
},
{
"_key" : "72500",
"_id" : "connections/72500",
"_from" : "places/Jasper",
"_to" : "places/Vancouver",
"_rev" : "_holfoG6--A",
"travelTime" : 12
},
{
"_key" : "72502",
"_id" : "connections/72502",
"_from" : "places/Vancouver",
"_to" : "places/Jasper",
"_rev" : "_holfoG6--B",
"travelTime" : 13
}
]Mps Graph
The mps_graph has been created to demonstrate shortest path algorithms and
the abbreviation stands for multiple path search.
The example graph consists of vertices in the mps_verts collection and edges
in the mps_edges collection. It is a simple traversal graph with start node
A and end node C.

With the Shortest Path algorithm, you either get the shortest path A - B - C or A - D - C. With the All Shortest Paths algorithm, both shortest paths are returned.
Example of how to create the graph, inspect its vertices and edges, and delete it again:
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var g = examples.loadGraph("mps_graph");
db.mps_verts.toArray();
db.mps_edges.toArray();
examples.dropGraph("mps_graph");Show output
[
{
"_key" : "A",
"_id" : "mps_verts/A",
"_rev" : "_holfoIW---"
},
{
"_key" : "B",
"_id" : "mps_verts/B",
"_rev" : "_holfoIa---"
},
{
"_key" : "C",
"_id" : "mps_verts/C",
"_rev" : "_holfoIa--_"
},
{
"_key" : "D",
"_id" : "mps_verts/D",
"_rev" : "_holfoIa--A"
},
{
"_key" : "E",
"_id" : "mps_verts/E",
"_rev" : "_holfoIa--B"
},
{
"_key" : "F",
"_id" : "mps_verts/F",
"_rev" : "_holfoIa--C"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "72550",
"_id" : "mps_edges/72550",
"_from" : "mps_verts/A",
"_to" : "mps_verts/B",
"_rev" : "_holfoIa--D",
"vertex" : "A"
},
{
"_key" : "72552",
"_id" : "mps_edges/72552",
"_from" : "mps_verts/A",
"_to" : "mps_verts/E",
"_rev" : "_holfoIe---",
"vertex" : "A"
},
{
"_key" : "72554",
"_id" : "mps_edges/72554",
"_from" : "mps_verts/A",
"_to" : "mps_verts/D",
"_rev" : "_holfoIe--_",
"vertex" : "A"
},
{
"_key" : "72556",
"_id" : "mps_edges/72556",
"_from" : "mps_verts/B",
"_to" : "mps_verts/C",
"_rev" : "_holfoIe--A",
"vertex" : "B"
},
{
"_key" : "72558",
"_id" : "mps_edges/72558",
"_from" : "mps_verts/D",
"_to" : "mps_verts/C",
"_rev" : "_holfoIe--B",
"vertex" : "D"
},
{
"_key" : "72560",
"_id" : "mps_edges/72560",
"_from" : "mps_verts/E",
"_to" : "mps_verts/F",
"_rev" : "_holfoIe--C",
"vertex" : "E"
},
{
"_key" : "72562",
"_id" : "mps_edges/72562",
"_from" : "mps_verts/F",
"_to" : "mps_verts/C",
"_rev" : "_holfoIi---",
"vertex" : "F"
}
]World Graph
The worldCountry graph has as node structure as follows:
world → continent → country → capital
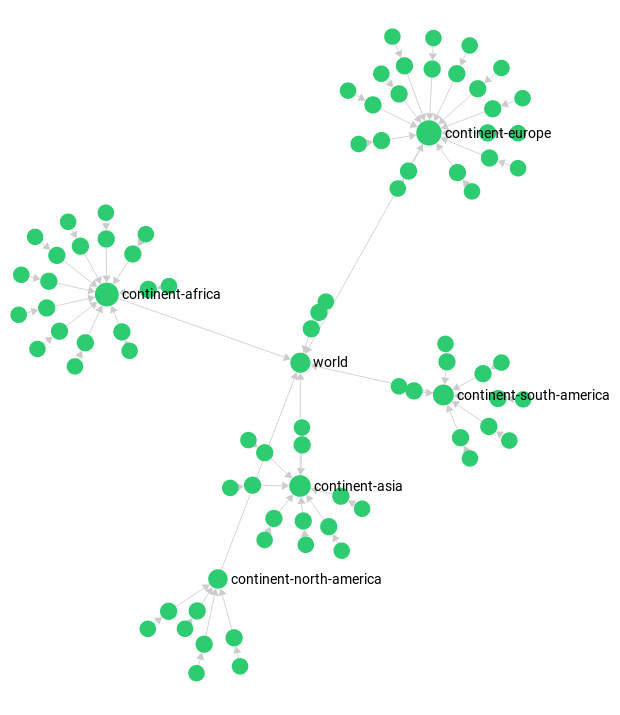
In some cases, edge directions aren’t forward. Therefore, it may get displayed disjunct in the graph viewer.
You can create the graph as a named graph using the name worldCountry, or as
an anonymous graph (vertex and edge collections only) using the name
worldCountryUnManaged.
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var g = examples.loadGraph("worldCountry");
db.worldVertices.toArray();
db.worldEdges.toArray();
examples.dropGraph("worldCountry");
var g = examples.loadGraph("worldCountryUnManaged");
examples.dropGraph("worldCountryUnManaged");Show output
[
{
"_key" : "world",
"_id" : "worldVertices/world",
"_rev" : "_holfoJq---",
"name" : "World",
"type" : "root"
},
{
"_key" : "continent-africa",
"_id" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoJq--_",
"name" : "Africa",
"type" : "continent"
},
{
"_key" : "continent-asia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_rev" : "_holfoJu---",
"name" : "Asia",
"type" : "continent"
},
{
"_key" : "continent-australia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/continent-australia",
"_rev" : "_holfoJu--_",
"name" : "Australia",
"type" : "continent"
},
{
"_key" : "continent-europe",
"_id" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoJu--A",
"name" : "Europe",
"type" : "continent"
},
{
"_key" : "continent-north-america",
"_id" : "worldVertices/continent-north-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoJu--B",
"name" : "North America",
"type" : "continent"
},
{
"_key" : "continent-south-america",
"_id" : "worldVertices/continent-south-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoJu--C",
"name" : "South America",
"type" : "continent"
},
{
"_key" : "country-afghanistan",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-afghanistan",
"_rev" : "_holfoJy---",
"name" : "Afghanistan",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "AFG"
},
{
"_key" : "country-albania",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-albania",
"_rev" : "_holfoJy--_",
"name" : "Albania",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "ALB"
},
{
"_key" : "country-algeria",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-algeria",
"_rev" : "_holfoJy--A",
"name" : "Algeria",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "DZA"
},
{
"_key" : "country-andorra",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-andorra",
"_rev" : "_holfoJy--B",
"name" : "Andorra",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "AND"
},
{
"_key" : "country-angola",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-angola",
"_rev" : "_holfoJy--C",
"name" : "Angola",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "AGO"
},
{
"_key" : "country-antigua-and-barbuda",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-antigua-and-barbuda",
"_rev" : "_holfoJy--D",
"name" : "Antigua and Barbuda",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "ATG"
},
{
"_key" : "country-argentina",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-argentina",
"_rev" : "_holfoJ2---",
"name" : "Argentina",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "ARG"
},
{
"_key" : "country-australia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-australia",
"_rev" : "_holfoJ2--_",
"name" : "Australia",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "AUS"
},
{
"_key" : "country-austria",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-austria",
"_rev" : "_holfoJ2--A",
"name" : "Austria",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "AUT"
},
{
"_key" : "country-bahamas",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-bahamas",
"_rev" : "_holfoJ2--B",
"name" : "Bahamas",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BHS"
},
{
"_key" : "country-bahrain",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-bahrain",
"_rev" : "_holfoJ2--C",
"name" : "Bahrain",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BHR"
},
{
"_key" : "country-bangladesh",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-bangladesh",
"_rev" : "_holfoJ6---",
"name" : "Bangladesh",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BGD"
},
{
"_key" : "country-barbados",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-barbados",
"_rev" : "_holfoJ6--_",
"name" : "Barbados",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BRB"
},
{
"_key" : "country-belgium",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-belgium",
"_rev" : "_holfoJ6--A",
"name" : "Belgium",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BEL"
},
{
"_key" : "country-bhutan",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-bhutan",
"_rev" : "_holfoK----",
"name" : "Bhutan",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BTN"
},
{
"_key" : "country-bolivia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-bolivia",
"_rev" : "_holfoK---_",
"name" : "Bolivia",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BOL"
},
{
"_key" : "country-bosnia-and-herzegovina",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-bosnia-and-herzegovina",
"_rev" : "_holfoK---A",
"name" : "Bosnia and Herzegovina",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BIH"
},
{
"_key" : "country-botswana",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-botswana",
"_rev" : "_holfoK---B",
"name" : "Botswana",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BWA"
},
{
"_key" : "country-brazil",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-brazil",
"_rev" : "_holfoK---C",
"name" : "Brazil",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BRA"
},
{
"_key" : "country-brunei",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-brunei",
"_rev" : "_holfoKC---",
"name" : "Brunei",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BRN"
},
{
"_key" : "country-bulgaria",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-bulgaria",
"_rev" : "_holfoKC--_",
"name" : "Bulgaria",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BGR"
},
{
"_key" : "country-burkina-faso",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-burkina-faso",
"_rev" : "_holfoKC--A",
"name" : "Burkina Faso",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BFA"
},
{
"_key" : "country-burundi",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-burundi",
"_rev" : "_holfoKC--B",
"name" : "Burundi",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "BDI"
},
{
"_key" : "country-cambodia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-cambodia",
"_rev" : "_holfoKC--C",
"name" : "Cambodia",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "KHM"
},
{
"_key" : "country-cameroon",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-cameroon",
"_rev" : "_holfoKC--D",
"name" : "Cameroon",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "CMR"
},
{
"_key" : "country-canada",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-canada",
"_rev" : "_holfoKC--E",
"name" : "Canada",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "CAN"
},
{
"_key" : "country-chad",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-chad",
"_rev" : "_holfoKG---",
"name" : "Chad",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "TCD"
},
{
"_key" : "country-chile",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-chile",
"_rev" : "_holfoKG--_",
"name" : "Chile",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "CHL"
},
{
"_key" : "country-colombia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-colombia",
"_rev" : "_holfoKG--A",
"name" : "Colombia",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "COL"
},
{
"_key" : "country-cote-d-ivoire",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-cote-d-ivoire",
"_rev" : "_holfoKG--B",
"name" : "Cote d'Ivoire",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "CIV"
},
{
"_key" : "country-croatia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-croatia",
"_rev" : "_holfoKG--C",
"name" : "Croatia",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "HRV"
},
{
"_key" : "country-czech-republic",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-czech-republic",
"_rev" : "_holfoKG--D",
"name" : "Czech Republic",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "CZE"
},
{
"_key" : "country-denmark",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-denmark",
"_rev" : "_holfoKG--E",
"name" : "Denmark",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "DNK"
},
{
"_key" : "country-ecuador",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-ecuador",
"_rev" : "_holfoKK---",
"name" : "Ecuador",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "ECU"
},
{
"_key" : "country-egypt",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-egypt",
"_rev" : "_holfoKK--_",
"name" : "Egypt",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "EGY"
},
{
"_key" : "country-eritrea",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-eritrea",
"_rev" : "_holfoKK--A",
"name" : "Eritrea",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "ERI"
},
{
"_key" : "country-finland",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-finland",
"_rev" : "_holfoKK--B",
"name" : "Finland",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "FIN"
},
{
"_key" : "country-france",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-france",
"_rev" : "_holfoKK--C",
"name" : "France",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "FRA"
},
{
"_key" : "country-germany",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-germany",
"_rev" : "_holfoKK--D",
"name" : "Germany",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "DEU"
},
{
"_key" : "country-people-s-republic-of-china",
"_id" : "worldVertices/country-people-s-republic-of-china",
"_rev" : "_holfoKO---",
"name" : "People's Republic of China",
"type" : "country",
"code" : "CHN"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-algiers",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-algiers",
"_rev" : "_holfoKO--_",
"name" : "Algiers",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-andorra-la-vella",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-andorra-la-vella",
"_rev" : "_holfoKO--A",
"name" : "Andorra la Vella",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-asmara",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-asmara",
"_rev" : "_holfoKO--B",
"name" : "Asmara",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-bandar-seri-begawan",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-bandar-seri-begawan",
"_rev" : "_holfoKO--C",
"name" : "Bandar Seri Begawan",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-beijing",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-beijing",
"_rev" : "_holfoKO--D",
"name" : "Beijing",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-berlin",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-berlin",
"_rev" : "_holfoKS---",
"name" : "Berlin",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-bogota",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-bogota",
"_rev" : "_holfoKS--_",
"name" : "Bogota",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-brasilia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-brasilia",
"_rev" : "_holfoKS--A",
"name" : "Brasilia",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-bridgetown",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-bridgetown",
"_rev" : "_holfoKS--B",
"name" : "Bridgetown",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-brussels",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-brussels",
"_rev" : "_holfoKS--C",
"name" : "Brussels",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-buenos-aires",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-buenos-aires",
"_rev" : "_holfoKS--D",
"name" : "Buenos Aires",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-bujumbura",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-bujumbura",
"_rev" : "_holfoKS--E",
"name" : "Bujumbura",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-cairo",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-cairo",
"_rev" : "_holfoKW---",
"name" : "Cairo",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-canberra",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-canberra",
"_rev" : "_holfoKW--_",
"name" : "Canberra",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-copenhagen",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-copenhagen",
"_rev" : "_holfoKW--A",
"name" : "Copenhagen",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-dhaka",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-dhaka",
"_rev" : "_holfoKW--B",
"name" : "Dhaka",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-gaborone",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-gaborone",
"_rev" : "_holfoKW--C",
"name" : "Gaborone",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-helsinki",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-helsinki",
"_rev" : "_holfoKa---",
"name" : "Helsinki",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-kabul",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-kabul",
"_rev" : "_holfoKa--_",
"name" : "Kabul",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-la-paz",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-la-paz",
"_rev" : "_holfoKa--A",
"name" : "La Paz",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-luanda",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-luanda",
"_rev" : "_holfoKa--B",
"name" : "Luanda",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-manama",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-manama",
"_rev" : "_holfoKa--C",
"name" : "Manama",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-nassau",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-nassau",
"_rev" : "_holfoKe---",
"name" : "Nassau",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-n-djamena",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-n-djamena",
"_rev" : "_holfoKe--_",
"name" : "N'Djamena",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-ottawa",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-ottawa",
"_rev" : "_holfoKe--A",
"name" : "Ottawa",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-ouagadougou",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-ouagadougou",
"_rev" : "_holfoKe--B",
"name" : "Ouagadougou",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-paris",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-paris",
"_rev" : "_holfoKe--C",
"name" : "Paris",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-phnom-penh",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-phnom-penh",
"_rev" : "_holfoKi---",
"name" : "Phnom Penh",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-prague",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-prague",
"_rev" : "_holfoKi--_",
"name" : "Prague",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-quito",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-quito",
"_rev" : "_holfoKi--A",
"name" : "Quito",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-saint-john-s",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-saint-john-s",
"_rev" : "_holfoKi--B",
"name" : "Saint John's",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-santiago",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-santiago",
"_rev" : "_holfoKi--C",
"name" : "Santiago",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-sarajevo",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-sarajevo",
"_rev" : "_holfoKi--D",
"name" : "Sarajevo",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-sofia",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-sofia",
"_rev" : "_holfoKm---",
"name" : "Sofia",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-thimphu",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-thimphu",
"_rev" : "_holfoKm--_",
"name" : "Thimphu",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-tirana",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-tirana",
"_rev" : "_holfoKm--A",
"name" : "Tirana",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-vienna",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-vienna",
"_rev" : "_holfoKm--B",
"name" : "Vienna",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-yamoussoukro",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-yamoussoukro",
"_rev" : "_holfoKm--C",
"name" : "Yamoussoukro",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-yaounde",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-yaounde",
"_rev" : "_holfoKq---",
"name" : "Yaounde",
"type" : "capital"
},
{
"_key" : "capital-zagreb",
"_id" : "worldVertices/capital-zagreb",
"_rev" : "_holfoKq--_",
"name" : "Zagreb",
"type" : "capital"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "72691",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72691",
"_from" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_to" : "worldVertices/world",
"_rev" : "_holfoKq--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72693",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72693",
"_from" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/world",
"_rev" : "_holfoKq--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72695",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72695",
"_from" : "worldVertices/continent-australia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/world",
"_rev" : "_holfoKq--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72697",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72697",
"_from" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_to" : "worldVertices/world",
"_rev" : "_holfoKq--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72699",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72699",
"_from" : "worldVertices/continent-north-america",
"_to" : "worldVertices/world",
"_rev" : "_holfoKq--E",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72701",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72701",
"_from" : "worldVertices/continent-south-america",
"_to" : "worldVertices/world",
"_rev" : "_holfoKu---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72703",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72703",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-afghanistan",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_rev" : "_holfoKu--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72705",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72705",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-albania",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoKu--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72707",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72707",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-algeria",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoKu--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72709",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72709",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-andorra",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoK6---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72711",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72711",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-angola",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoK6--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72713",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72713",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-antigua-and-barbuda",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-north-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoK6--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72715",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72715",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-argentina",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-south-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoL----",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72717",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72717",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-australia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-australia",
"_rev" : "_holfoL---_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72719",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72719",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-austria",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoL---A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72721",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72721",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-bahamas",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-north-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoL---B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72723",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72723",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-bahrain",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_rev" : "_holfoL---C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72725",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72725",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-bangladesh",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_rev" : "_holfoL---D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72727",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72727",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-barbados",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-north-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoLC---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72729",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72729",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-belgium",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLC--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72731",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72731",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-bhutan",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLC--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72733",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72733",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-bolivia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-south-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoLC--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72735",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72735",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-bosnia-and-herzegovina",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLC--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72737",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72737",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-botswana",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoLG---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72739",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72739",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-brazil",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-south-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoLG--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72741",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72741",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-brunei",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLG--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72743",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72743",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-bulgaria",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLG--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72745",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72745",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-burkina-faso",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoLG--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72747",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72747",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-burundi",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoLG--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72749",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72749",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-cambodia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLK---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72751",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72751",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-cameroon",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoLK--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72753",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72753",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-canada",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-north-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoLK--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72755",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72755",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-chad",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoLK--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72757",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72757",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-chile",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-south-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoLK--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72759",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72759",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-colombia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-south-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoLK--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72761",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72761",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-cote-d-ivoire",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoLO---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72763",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72763",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-croatia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLO--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72765",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72765",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-czech-republic",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLO--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72767",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72767",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-denmark",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLO--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72769",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72769",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-ecuador",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-south-america",
"_rev" : "_holfoLO--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72771",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72771",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-egypt",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoLO--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72773",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72773",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-eritrea",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-africa",
"_rev" : "_holfoLS---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72775",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72775",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-finland",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLS--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72777",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72777",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-france",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLS--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72779",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72779",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-germany",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-europe",
"_rev" : "_holfoLS--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72781",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72781",
"_from" : "worldVertices/country-people-s-republic-of-china",
"_to" : "worldVertices/continent-asia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLS--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72783",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72783",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-algiers",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-algeria",
"_rev" : "_holfoLS--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72785",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72785",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-andorra-la-vella",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-andorra",
"_rev" : "_holfoLW---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72787",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72787",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-asmara",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-eritrea",
"_rev" : "_holfoLW--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72789",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72789",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-bandar-seri-begawan",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-brunei",
"_rev" : "_holfoLW--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72791",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72791",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-beijing",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-people-s-republic-of-china",
"_rev" : "_holfoLW--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72793",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72793",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-berlin",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-germany",
"_rev" : "_holfoLW--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72795",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72795",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-bogota",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-colombia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLa---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72797",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72797",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-brasilia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-brazil",
"_rev" : "_holfoLa--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72799",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72799",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-bridgetown",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-barbados",
"_rev" : "_holfoLa--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72801",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72801",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-brussels",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-belgium",
"_rev" : "_holfoLa--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72803",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72803",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-buenos-aires",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-argentina",
"_rev" : "_holfoLa--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72805",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72805",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-bujumbura",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-burundi",
"_rev" : "_holfoLa--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72807",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72807",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-cairo",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-egypt",
"_rev" : "_holfoLe---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72809",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72809",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-canberra",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-australia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLe--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72811",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72811",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-copenhagen",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-denmark",
"_rev" : "_holfoLe--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72813",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72813",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-dhaka",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-bangladesh",
"_rev" : "_holfoLe--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72815",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72815",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-gaborone",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-botswana",
"_rev" : "_holfoLe--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72817",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72817",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-helsinki",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-finland",
"_rev" : "_holfoLi---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72819",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72819",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-kabul",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-afghanistan",
"_rev" : "_holfoLi--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72821",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72821",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-la-paz",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-bolivia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLi--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72823",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72823",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-luanda",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-angola",
"_rev" : "_holfoLi--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72825",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72825",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-manama",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-bahrain",
"_rev" : "_holfoLi--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72827",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72827",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-nassau",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-bahamas",
"_rev" : "_holfoLi--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72829",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72829",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-n-djamena",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-chad",
"_rev" : "_holfoLi--E",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72831",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72831",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-ottawa",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-canada",
"_rev" : "_holfoLm---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72833",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72833",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-ouagadougou",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-burkina-faso",
"_rev" : "_holfoLm--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72835",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72835",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-paris",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-france",
"_rev" : "_holfoLm--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72837",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72837",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-phnom-penh",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-cambodia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLm--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72839",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72839",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-prague",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-czech-republic",
"_rev" : "_holfoLm--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72841",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72841",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-quito",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-ecuador",
"_rev" : "_holfoLm--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72843",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72843",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-saint-john-s",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-antigua-and-barbuda",
"_rev" : "_holfoLq---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72845",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72845",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-santiago",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-chile",
"_rev" : "_holfoLq--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72847",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72847",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-sarajevo",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-bosnia-and-herzegovina",
"_rev" : "_holfoLq--A",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72849",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72849",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-sofia",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-bulgaria",
"_rev" : "_holfoLq--B",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72851",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72851",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-thimphu",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-bhutan",
"_rev" : "_holfoLq--C",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72853",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72853",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-tirana",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-albania",
"_rev" : "_holfoLq--D",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72855",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72855",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-vienna",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-austria",
"_rev" : "_holfoLq--E",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72857",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72857",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-yamoussoukro",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-cote-d-ivoire",
"_rev" : "_holfoLu---",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72859",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72859",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-yaounde",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-cameroon",
"_rev" : "_holfoLu--_",
"type" : "is-in"
},
{
"_key" : "72861",
"_id" : "worldEdges/72861",
"_from" : "worldVertices/capital-zagreb",
"_to" : "worldVertices/country-croatia",
"_rev" : "_holfoLu--A",
"type" : "is-in"
}
]Social Graph
The social graph is a set of persons and their relations. The graph has
female and male persons as vertices in two vertex collections.
The edges are their connections and stored in the relation edge collection.
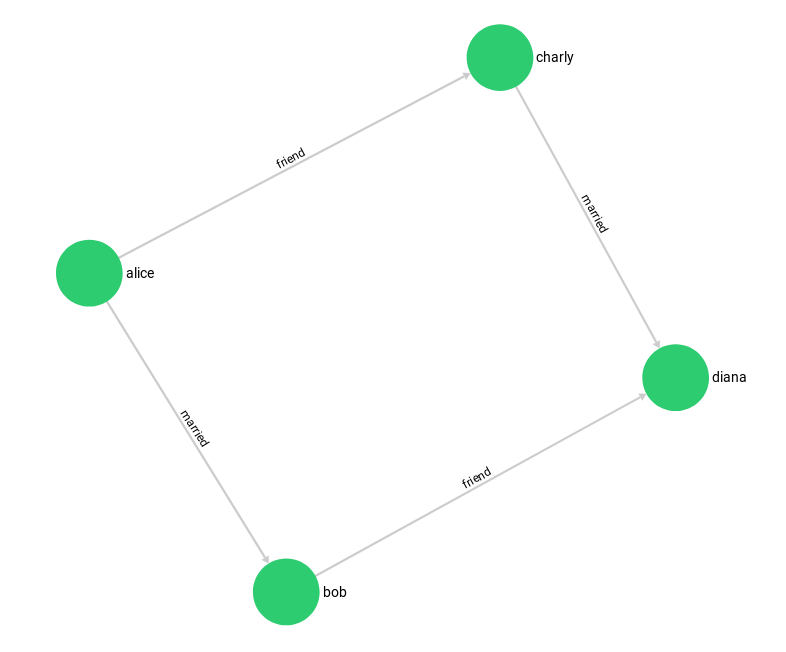
Example of how to create the graph, inspect its vertices and edges, and delete it again:
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
db.female.toArray()
db.male.toArray()
db.relation.toArray()
examples.dropGraph("social");Show output
[
{
"_key" : "alice",
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_rev" : "_holfoRW---",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_key" : "diana",
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_rev" : "_holfoRa--A",
"name" : "Diana"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "bob",
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_rev" : "_holfoRa---",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_key" : "charly",
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_rev" : "_holfoRa--_",
"name" : "Charly"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "73187",
"_id" : "relation/73187",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"_rev" : "_holfoRa--B",
"type" : "married",
"vertex" : "alice"
},
{
"_key" : "73189",
"_id" : "relation/73189",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/charly",
"_rev" : "_holfoRa--C",
"type" : "friend",
"vertex" : "alice"
},
{
"_key" : "73191",
"_id" : "relation/73191",
"_from" : "male/charly",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"_rev" : "_holfoRa--D",
"type" : "married",
"vertex" : "charly"
},
{
"_key" : "73193",
"_id" : "relation/73193",
"_from" : "male/bob",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"_rev" : "_holfoRa--E",
"type" : "friend",
"vertex" : "bob"
}
]City Graph
The routeplanner graph is a set of european cities and their fictional
traveling distances as connections. The graph has the cities as vertices in
multiple vertex collections (germanCity and frenchCity). The edges are their
interconnections in several edge collections (frenchHighway, germanHighway,
internationalHighway).
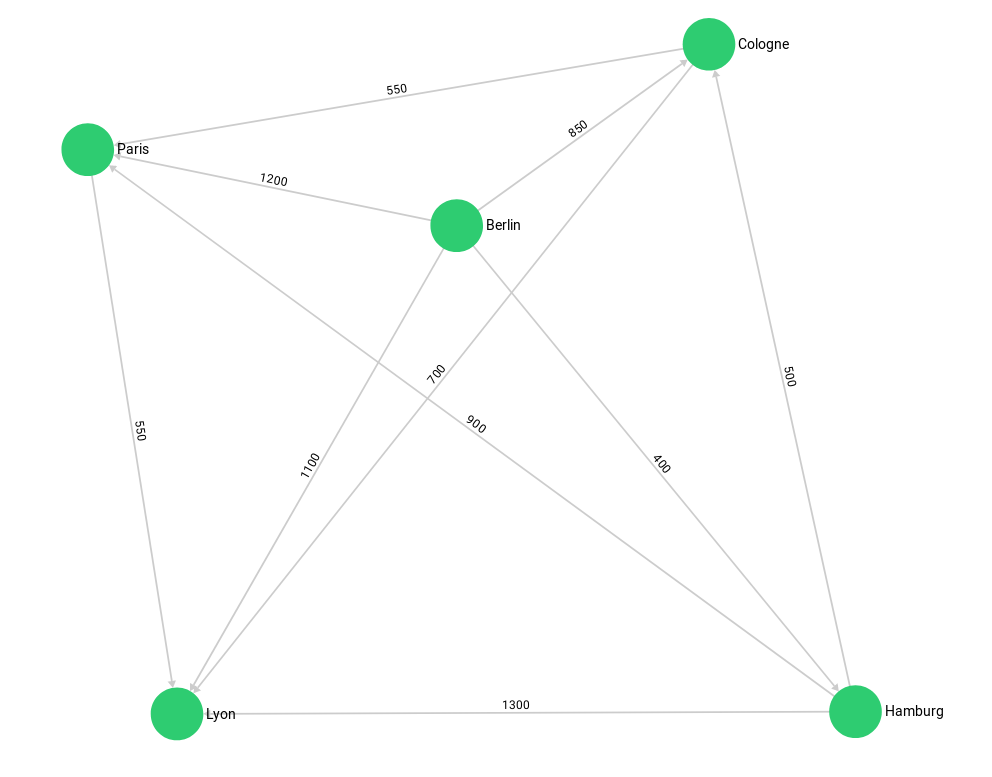
Example of how to create the graph, inspect its edges and vertices, and delete it again:
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var g = examples.loadGraph("routeplanner");
db.frenchCity.toArray();
db.germanCity.toArray();
db.germanHighway.toArray();
db.frenchHighway.toArray();
db.internationalHighway.toArray();
examples.dropGraph("routeplanner");Show output
[
{
"_key" : "Lyon",
"_id" : "frenchCity/Lyon",
"_rev" : "_holfoTO---",
"population" : 80000,
"isCapital" : false,
"geometry" : {
"type" : "Point",
"coordinates" : [
4.84,
45.76
]
}
},
{
"_key" : "Paris",
"_id" : "frenchCity/Paris",
"_rev" : "_holfoTO--_",
"population" : 4000000,
"isCapital" : true,
"geometry" : {
"type" : "Point",
"coordinates" : [
2.3508,
48.8567
]
}
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "Berlin",
"_id" : "germanCity/Berlin",
"_rev" : "_holfoTK---",
"population" : 3000000,
"isCapital" : true,
"geometry" : {
"type" : "Point",
"coordinates" : [
13.3833,
52.5167
]
}
},
{
"_key" : "Cologne",
"_id" : "germanCity/Cologne",
"_rev" : "_holfoTK--_",
"population" : 1000000,
"isCapital" : false,
"geometry" : {
"type" : "Point",
"coordinates" : [
6.9528,
50.9364
]
}
},
{
"_key" : "Hamburg",
"_id" : "germanCity/Hamburg",
"_rev" : "_holfoTK--A",
"population" : 1000000,
"isCapital" : false,
"geometry" : {
"type" : "Point",
"coordinates" : [
10.0014,
53.5653
]
}
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "73269",
"_id" : "germanHighway/73269",
"_from" : "germanCity/Berlin",
"_to" : "germanCity/Cologne",
"_rev" : "_holfoTS--_",
"distance" : 850
},
{
"_key" : "73271",
"_id" : "germanHighway/73271",
"_from" : "germanCity/Berlin",
"_to" : "germanCity/Hamburg",
"_rev" : "_holfoTS--A",
"distance" : 400
},
{
"_key" : "73273",
"_id" : "germanHighway/73273",
"_from" : "germanCity/Hamburg",
"_to" : "germanCity/Cologne",
"_rev" : "_holfoTS--B",
"distance" : 500
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "73275",
"_id" : "frenchHighway/73275",
"_from" : "frenchCity/Paris",
"_to" : "frenchCity/Lyon",
"_rev" : "_holfoTW---",
"distance" : 550
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "73277",
"_id" : "internationalHighway/73277",
"_from" : "germanCity/Berlin",
"_to" : "frenchCity/Lyon",
"_rev" : "_holfoTW--_",
"distance" : 1100
},
{
"_key" : "73279",
"_id" : "internationalHighway/73279",
"_from" : "germanCity/Berlin",
"_to" : "frenchCity/Paris",
"_rev" : "_holfoTW--A",
"distance" : 1200
},
{
"_key" : "73281",
"_id" : "internationalHighway/73281",
"_from" : "germanCity/Hamburg",
"_to" : "frenchCity/Paris",
"_rev" : "_holfoTW--B",
"distance" : 900
},
{
"_key" : "73283",
"_id" : "internationalHighway/73283",
"_from" : "germanCity/Hamburg",
"_to" : "frenchCity/Lyon",
"_rev" : "_holfoTW--C",
"distance" : 1300
},
{
"_key" : "73285",
"_id" : "internationalHighway/73285",
"_from" : "germanCity/Cologne",
"_to" : "frenchCity/Lyon",
"_rev" : "_holfoTW--D",
"distance" : 700
},
{
"_key" : "73287",
"_id" : "internationalHighway/73287",
"_from" : "germanCity/Cologne",
"_to" : "frenchCity/Paris",
"_rev" : "_holfoTW--E",
"distance" : 550
}
]Connected Components Graph
A small example graph comprised of components (vertices) and connections
(edges). Good for trying out Pregel algorithms such as Weakly Connected
Components (WCC).
Also see:
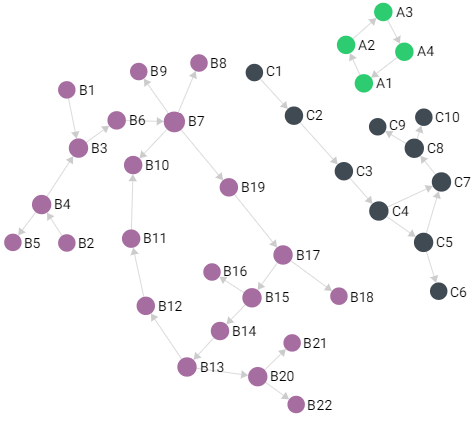
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var g = examples.loadGraph("connectedComponentsGraph");
db.components.toArray();
db.connections.toArray();
examples.dropGraph("connectedComponentsGraph");Show output
[
{
"_key" : "A1",
"_id" : "components/A1",
"_rev" : "_holfoUW---"
},
{
"_key" : "A2",
"_id" : "components/A2",
"_rev" : "_holfoUW--_"
},
{
"_key" : "A3",
"_id" : "components/A3",
"_rev" : "_holfoUa---"
},
{
"_key" : "A4",
"_id" : "components/A4",
"_rev" : "_holfoUe---"
},
{
"_key" : "B1",
"_id" : "components/B1",
"_rev" : "_holfoUe--_"
},
{
"_key" : "B3",
"_id" : "components/B3",
"_rev" : "_holfoUe--A"
},
{
"_key" : "B2",
"_id" : "components/B2",
"_rev" : "_holfoUe--B"
},
{
"_key" : "B4",
"_id" : "components/B4",
"_rev" : "_holfoUe--C"
},
{
"_key" : "B6",
"_id" : "components/B6",
"_rev" : "_holfoUe--D"
},
{
"_key" : "B5",
"_id" : "components/B5",
"_rev" : "_holfoUi---"
},
{
"_key" : "B7",
"_id" : "components/B7",
"_rev" : "_holfoUi--_"
},
{
"_key" : "B8",
"_id" : "components/B8",
"_rev" : "_holfoUi--A"
},
{
"_key" : "B9",
"_id" : "components/B9",
"_rev" : "_holfoUi--B"
},
{
"_key" : "B10",
"_id" : "components/B10",
"_rev" : "_holfoUi--C"
},
{
"_key" : "B19",
"_id" : "components/B19",
"_rev" : "_holfoUm---"
},
{
"_key" : "B11",
"_id" : "components/B11",
"_rev" : "_holfoUm--_"
},
{
"_key" : "B12",
"_id" : "components/B12",
"_rev" : "_holfoUm--A"
},
{
"_key" : "B13",
"_id" : "components/B13",
"_rev" : "_holfoUm--B"
},
{
"_key" : "B20",
"_id" : "components/B20",
"_rev" : "_holfoUm--C"
},
{
"_key" : "B14",
"_id" : "components/B14",
"_rev" : "_holfoUq---"
},
{
"_key" : "B15",
"_id" : "components/B15",
"_rev" : "_holfoUq--_"
},
{
"_key" : "B16",
"_id" : "components/B16",
"_rev" : "_holfoUq--A"
},
{
"_key" : "B17",
"_id" : "components/B17",
"_rev" : "_holfoUq--B"
},
{
"_key" : "B18",
"_id" : "components/B18",
"_rev" : "_holfoUq--C"
},
{
"_key" : "B21",
"_id" : "components/B21",
"_rev" : "_holfoUu---"
},
{
"_key" : "B22",
"_id" : "components/B22",
"_rev" : "_holfoUu--_"
},
{
"_key" : "C1",
"_id" : "components/C1",
"_rev" : "_holfoUu--A"
},
{
"_key" : "C2",
"_id" : "components/C2",
"_rev" : "_holfoUu--B"
},
{
"_key" : "C3",
"_id" : "components/C3",
"_rev" : "_holfoUu--C"
},
{
"_key" : "C4",
"_id" : "components/C4",
"_rev" : "_holfoUu--D"
},
{
"_key" : "C5",
"_id" : "components/C5",
"_rev" : "_holfoUy---"
},
{
"_key" : "C7",
"_id" : "components/C7",
"_rev" : "_holfoUy--_"
},
{
"_key" : "C6",
"_id" : "components/C6",
"_rev" : "_holfoUy--A"
},
{
"_key" : "C8",
"_id" : "components/C8",
"_rev" : "_holfoUy--B"
},
{
"_key" : "C9",
"_id" : "components/C9",
"_rev" : "_holfoUy--C"
},
{
"_key" : "C10",
"_id" : "components/C10",
"_rev" : "_holfoUy--D"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "73389",
"_id" : "connections/73389",
"_from" : "components/A1",
"_to" : "components/A2",
"_rev" : "_holfoUy--E"
},
{
"_key" : "73391",
"_id" : "connections/73391",
"_from" : "components/A2",
"_to" : "components/A3",
"_rev" : "_holfoU2---"
},
{
"_key" : "73393",
"_id" : "connections/73393",
"_from" : "components/A3",
"_to" : "components/A4",
"_rev" : "_holfoU2--_"
},
{
"_key" : "73395",
"_id" : "connections/73395",
"_from" : "components/A4",
"_to" : "components/A1",
"_rev" : "_holfoU2--A"
},
{
"_key" : "73397",
"_id" : "connections/73397",
"_from" : "components/B1",
"_to" : "components/B3",
"_rev" : "_holfoU2--B"
},
{
"_key" : "73399",
"_id" : "connections/73399",
"_from" : "components/B2",
"_to" : "components/B4",
"_rev" : "_holfoU6---"
},
{
"_key" : "73401",
"_id" : "connections/73401",
"_from" : "components/B3",
"_to" : "components/B6",
"_rev" : "_holfoU6--_"
},
{
"_key" : "73403",
"_id" : "connections/73403",
"_from" : "components/B4",
"_to" : "components/B3",
"_rev" : "_holfoU6--A"
},
{
"_key" : "73405",
"_id" : "connections/73405",
"_from" : "components/B4",
"_to" : "components/B5",
"_rev" : "_holfoU6--B"
},
{
"_key" : "73407",
"_id" : "connections/73407",
"_from" : "components/B6",
"_to" : "components/B7",
"_rev" : "_holfoU6--C"
},
{
"_key" : "73409",
"_id" : "connections/73409",
"_from" : "components/B7",
"_to" : "components/B8",
"_rev" : "_holfoU6--D"
},
{
"_key" : "73411",
"_id" : "connections/73411",
"_from" : "components/B7",
"_to" : "components/B9",
"_rev" : "_holfoV----"
},
{
"_key" : "73413",
"_id" : "connections/73413",
"_from" : "components/B7",
"_to" : "components/B10",
"_rev" : "_holfoV---_"
},
{
"_key" : "73415",
"_id" : "connections/73415",
"_from" : "components/B7",
"_to" : "components/B19",
"_rev" : "_holfoV---A"
},
{
"_key" : "73417",
"_id" : "connections/73417",
"_from" : "components/B11",
"_to" : "components/B10",
"_rev" : "_holfoV---B"
},
{
"_key" : "73419",
"_id" : "connections/73419",
"_from" : "components/B12",
"_to" : "components/B11",
"_rev" : "_holfoV---C"
},
{
"_key" : "73421",
"_id" : "connections/73421",
"_from" : "components/B13",
"_to" : "components/B12",
"_rev" : "_holfoV---D"
},
{
"_key" : "73423",
"_id" : "connections/73423",
"_from" : "components/B13",
"_to" : "components/B20",
"_rev" : "_holfoVC---"
},
{
"_key" : "73425",
"_id" : "connections/73425",
"_from" : "components/B14",
"_to" : "components/B13",
"_rev" : "_holfoVC--_"
},
{
"_key" : "73427",
"_id" : "connections/73427",
"_from" : "components/B15",
"_to" : "components/B14",
"_rev" : "_holfoVC--A"
},
{
"_key" : "73429",
"_id" : "connections/73429",
"_from" : "components/B15",
"_to" : "components/B16",
"_rev" : "_holfoVC--B"
},
{
"_key" : "73431",
"_id" : "connections/73431",
"_from" : "components/B17",
"_to" : "components/B15",
"_rev" : "_holfoVC--C"
},
{
"_key" : "73433",
"_id" : "connections/73433",
"_from" : "components/B17",
"_to" : "components/B18",
"_rev" : "_holfoVC--D"
},
{
"_key" : "73435",
"_id" : "connections/73435",
"_from" : "components/B19",
"_to" : "components/B17",
"_rev" : "_holfoVG---"
},
{
"_key" : "73437",
"_id" : "connections/73437",
"_from" : "components/B20",
"_to" : "components/B21",
"_rev" : "_holfoVG--_"
},
{
"_key" : "73439",
"_id" : "connections/73439",
"_from" : "components/B20",
"_to" : "components/B22",
"_rev" : "_holfoVG--A"
},
{
"_key" : "73441",
"_id" : "connections/73441",
"_from" : "components/C1",
"_to" : "components/C2",
"_rev" : "_holfoVG--B"
},
{
"_key" : "73443",
"_id" : "connections/73443",
"_from" : "components/C2",
"_to" : "components/C3",
"_rev" : "_holfoVG--C"
},
{
"_key" : "73445",
"_id" : "connections/73445",
"_from" : "components/C3",
"_to" : "components/C4",
"_rev" : "_holfoVK---"
},
{
"_key" : "73447",
"_id" : "connections/73447",
"_from" : "components/C4",
"_to" : "components/C5",
"_rev" : "_holfoVK--_"
},
{
"_key" : "73449",
"_id" : "connections/73449",
"_from" : "components/C4",
"_to" : "components/C7",
"_rev" : "_holfoVK--A"
},
{
"_key" : "73451",
"_id" : "connections/73451",
"_from" : "components/C5",
"_to" : "components/C6",
"_rev" : "_holfoVK--B"
},
{
"_key" : "73453",
"_id" : "connections/73453",
"_from" : "components/C5",
"_to" : "components/C7",
"_rev" : "_holfoVK--C"
},
{
"_key" : "73455",
"_id" : "connections/73455",
"_from" : "components/C7",
"_to" : "components/C8",
"_rev" : "_holfoVO---"
},
{
"_key" : "73457",
"_id" : "connections/73457",
"_from" : "components/C8",
"_to" : "components/C9",
"_rev" : "_holfoVO--_"
},
{
"_key" : "73459",
"_id" : "connections/73459",
"_from" : "components/C8",
"_to" : "components/C10",
"_rev" : "_holfoVO--A"
}
]Higher volume graph examples
All of the above examples are rather small to make them easy to comprehend and demonstrate how graphs work in ArangoDB. However, there are several, freely available datasets on the web that are a lot bigger.
You can find a collection of datasets with import scripts on GitHub .
Another huge graph is the Pokec social network from Slovakia. See this blogpost for details and an import script.
