ArangoDB v3.13 is under development and not released yet. This documentation is not final and potentially incomplete.
General Graphs
The basic type of a named graph is called a General Graph and there is a JavaScript module for working with these graphs
This chapter describes the general-graph module. It allows you to define a graph that is spread across several edge and document collections. This allows you to structure your models in line with your domain and group them logically in collections giving you the power to query them in the same graph queries. There is no need to include the referenced collections within the query, this module will handle it for you.
New to ArangoDB? Take the free ArangoDB Graph Course for freshers.
Getting started
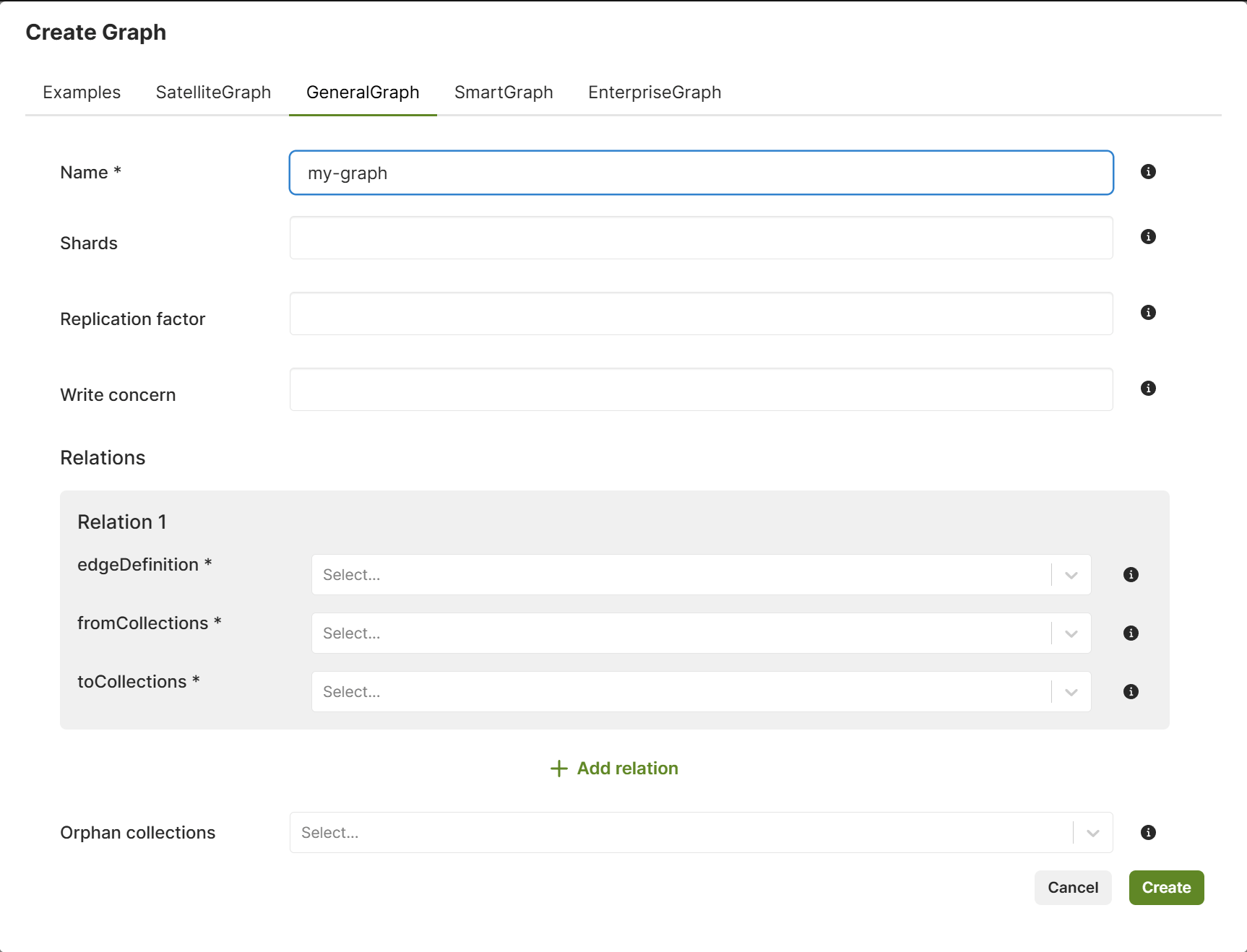
Create a General Graph using the web interface
The web interface (also called Web UI) allows you to easily create and manage General Graphs. To get started, follow the steps outlined below.
- In the web interface, navigate to the Graphs section.
- To add a new graph, click Add Graph.
- In the Create Graph dialog that appears, select the GeneralGraph tab.
- Fill in the following fields:
- For Name, enter a name for the General Graph.
- For Shards, enter the number of parts to split the graph into.
- For Replication factor, enter the total number of desired copies of the data in the cluster.
- For Write concern, enter the total number of copies of the data in the cluster required for each write operation.
- Define the relation(s) on the General Graph:
- For Edge definition, insert a single non-existent name to define
the relation of the graph. This automatically creates a new edge
collection, which is displayed in the Collections section of the
left sidebar menu.To define multiple relations, press the Add relation button. To remove a relation, press the Remove relation button.
- For fromCollections, insert a list of vertex collections that contain the start vertices of the relation.
- For toCollections, insert a list of vertex collections that contain the end vertices of the relation.
- For Edge definition, insert a single non-existent name to define
the relation of the graph. This automatically creates a new edge
collection, which is displayed in the Collections section of the
left sidebar menu.
- If you want to use vertex collections that are part of the graph but not used in any edge definition, you can insert them via Orphan collections.
- Click Create.
- Click the card of the newly created graph and use the functions of the Graph Viewer to visually interact with the graph and manage the graph data.
Create a General Graph using arangosh
Create a graph
var graph_module = require("@arangodb/general-graph");
var graph = graph_module._create("myGraph");
graph;Add some vertex collections
graph._addVertexCollection("shop");
graph._addVertexCollection("customer");
graph._addVertexCollection("pet");
graph = graph_module._graph("myGraph");Define relations on the Graph
var rel = graph_module._relation("isCustomer", ["shop"], ["customer"]);
graph._extendEdgeDefinitions(rel);
graph = graph_module._graph("myGraph");
