ArangoDB v3.13 is under development and not released yet. This documentation is not final and potentially incomplete.
Getting started with SmartGraphs
How to create and use SmartGraphs
SmartGraphs cannot use existing collections. When switching to SmartGraph from an existing dataset you have to import the data into a fresh SmartGraph.
All collections that are being used in SmartGraphs need to be part of the same
distributeShardslike group. The smartGraphAttribute and the number of
shards are immutable.
The smartGraphAttribute attribute is used to inform the database how to shard
data and, as a consequence, all nodes must have this attribute. The _from
and _to attributes that point from one document to another document
stored in node collections are set by default, following the same smart
sharding pattern.
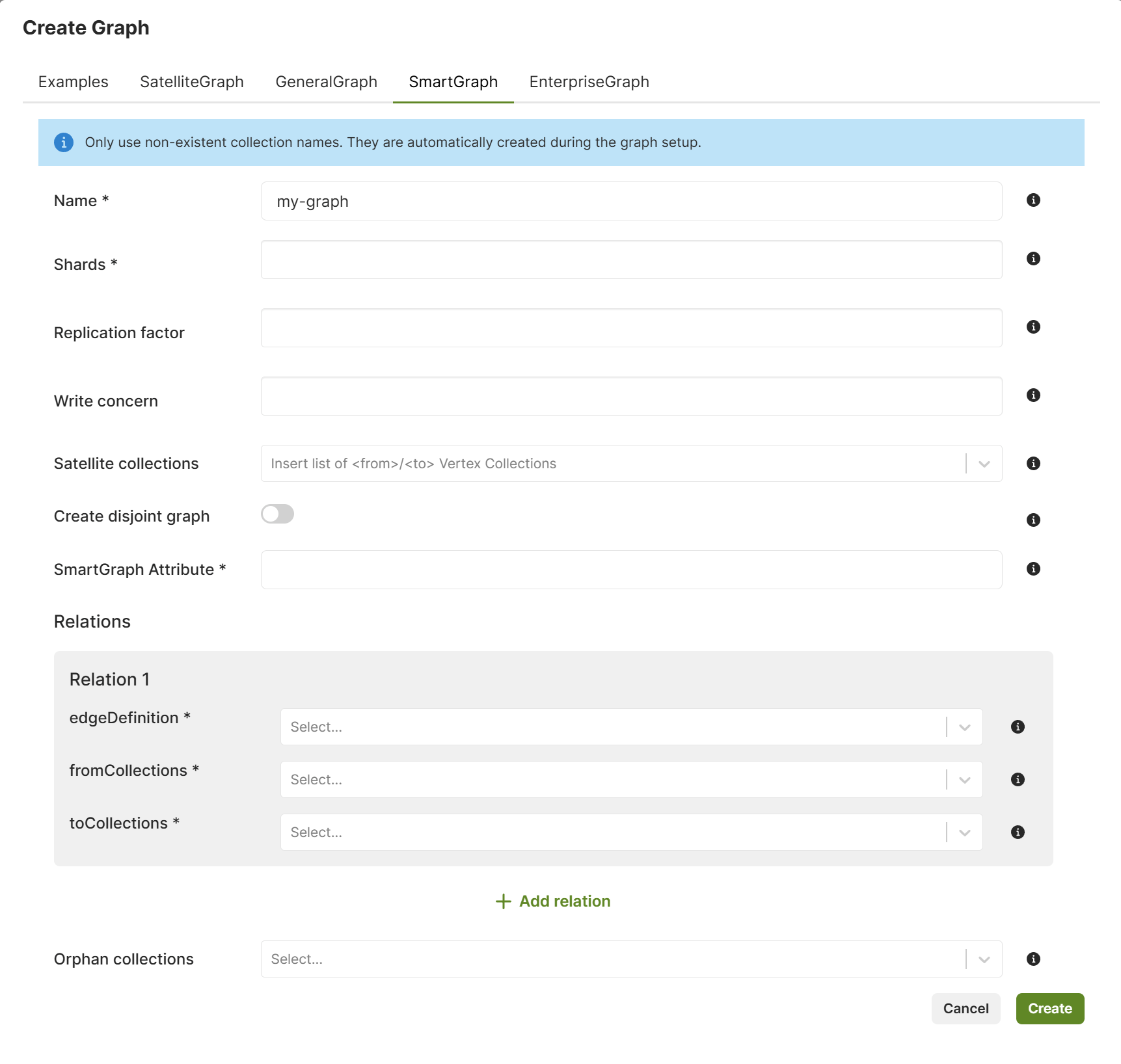
Create a SmartGraph using the web interface
The web interface (also called Web UI) allows you to easily create and manage SmartGraphs. To get started, follow the steps outlined below.
- In the web interface, navigate to the Graphs section.
- To add a new graph, click Add Graph.
- In the Create Graph dialog that appears, select the SmartGraph tab.
- Fill in all the following fields:
- For Name, enter a name for the SmartGraph.
- For Shards, enter the number of parts to split the graph into.
- Optional: For Replication factor, enter the total number of desired copies of the data in the cluster.
- Optional: For Write concern, enter the total number of copies of the data in the cluster required for each write operation.
- For SmartGraph Attribute, insert the attribute that is used to smartly shard the nodes of the graph. Every node in your graph needs to have this attribute. Note that it cannot be modified later.
- Optional: For SatelliteCollections, insert node collections that are used in your edge definitions. These collections are then created as satellites, and thus replicated to all DB-Servers.
- Define the relations on the graph:
- For Edge definition, insert a single non-existent name to define
the relation of the graph. This automatically creates a new edge
collection, which is displayed in the Collections section of the
left sidebar menu.To define multiple relations, press the Add relation button. To remove a relation, press the Remove relation button.
- For fromCollections, insert a list of node collections that contain the start nodes of the relation.
- For toCollections, insert a list of node collections that
contain the end nodes of the relation.Insert only non-existent collection names. Collections are automatically created during the graph setup and are displayed in the Collections tab of the left sidebar menu.
- For Orphan collections, insert a list of node collections that are part of the graph but not used in any edge definition.
- For Edge definition, insert a single non-existent name to define
the relation of the graph. This automatically creates a new edge
collection, which is displayed in the Collections section of the
left sidebar menu.
- Click Create.
- Click the name or row of the newly created graph to open the Graph Viewer if you want to visually interact with the graph and manage the graph data.
Create a SmartGraph using arangosh
In contrast to General Graphs we have to add more options when creating the
SmartGraph. The two options smartGraphAttribute and numberOfShards are
required and cannot be modified later.
var graph_module = require("@arangodb/smart-graph");
var graph = graph_module._create("myGraph", [], [], {smartGraphAttribute: "region", numberOfShards: 9});
graph;Show output
{[SmartGraph]
}Create a Disjoint SmartGraph using arangosh
In contrast to regular SmartGraphs we have to add one option when creating the
graph. The boolean option isDisjoint is required, needs to be set to true
and cannot be modified later.
var graph_module = require("@arangodb/smart-graph");
var graph = graph_module._create("myGraph", [], [], {smartGraphAttribute: "region", numberOfShards: 9, isDisjoint: true});
graph;Show output
{[SmartGraph]
}Add node collections
This is analogous to General Graphs. Unlike with General Graphs, the collections must not exist when creating the SmartGraph. The SmartGraph module will create them for you automatically to set up the sharding for all these collections correctly. If you create collections via the SmartGraph module and remove them from the graph definition, then you may re-add them without trouble however, as they will have the correct sharding.
graph._addVertexCollection("shop");
graph._addVertexCollection("customer");
graph._addVertexCollection("pet");
graph = graph_module._graph("myGraph");Show output
{[SmartGraph]
"customer" : [ArangoCollection 6011035, "customer" (type document, status loaded)],
"pet" : [ArangoCollection 6011046, "pet" (type document, status loaded)],
"shop" : [ArangoCollection 6011024, "shop" (type document, status loaded)]
}Define relations on the Graph
Adding edge collections works the same as with General Graphs, but again, the collections are created by the SmartGraph module to set up sharding correctly so they must not exist when creating the SmartGraph (unless they have the correct sharding already).
var rel = graph_module._relation("isCustomer", ["shop"], ["customer"]);
graph._extendEdgeDefinitions(rel);
graph = graph_module._graph("myGraph");Show output
{[SmartGraph]
"isCustomer" : [ArangoCollection 6011163, "isCustomer" (type edge, status loaded)],
"shop" : [ArangoCollection 6011129, "shop" (type document, status loaded)],
"customer" : [ArangoCollection 6011140, "customer" (type document, status loaded)],
"pet" : [ArangoCollection 6011151, "pet" (type document, status loaded)]
}Using SatelliteCollections in SmartGraphs
When creating a collection, you can decide whether it’s a SatelliteCollection
or not. For example, a node collection can be satellite as well.
SatelliteCollections don’t require sharding as the data will be distributed
globally on all DB-Servers. The smartGraphAttribute is also not required.
Create a SmartGraph using SatelliteCollections
In addition to the attributes you would set to create a SmartGraph, there is an
additional attribute satellites you can optionally set. It needs to be an array of
one or more collection names. These names can be used in edge definitions
(relations) and these collections will be created as SatelliteCollections.
However, all node collections on one side of the relation have to be of
the same type - either all satellite or all smart. This is because _from
and _to can have different types based on the sharding pattern.
In this example, both node collections are created as SatelliteCollections.
var graph_module = require("@arangodb/smart-graph");
var rel = graph_module._relation("isCustomer", "shop", "customer")
var graph = graph_module._create("myGraph", [rel], [], {satellites: ["shop", "customer"], smartGraphAttribute: "region", numberOfShards: 9});
graph;Show output
{[SmartGraph]
"isCustomer" : [ArangoCollection 6011294, "isCustomer" (type edge, status loaded)],
"shop" : [ArangoCollection 6011292, "shop" (type document, status loaded)],
"customer" : [ArangoCollection 6011293, "customer" (type document, status loaded)]
}Create a Disjoint SmartGraph using SatelliteCollections
The option isDisjoint needs to be set to true in addition to the other
options for a SmartGraph using SatelliteCollections. Only the shop node collection is created
as a SatelliteCollection in this example:
var graph_module = require("@arangodb/smart-graph");
var rel = graph_module._relation("isCustomer", "shop", "customer")
var graph = graph_module._create("myGraph", [rel], [], {satellites: ["shop"], smartGraphAttribute: "region", isDisjoint: true, numberOfShards: 9});
graph;Show output
{[SmartGraph]
"isCustomer" : [ArangoCollection 6011368, "isCustomer" (type edge, status loaded)],
"shop" : [ArangoCollection 6011366, "shop" (type document, status loaded)],
"customer" : [ArangoCollection 6011367, "customer" (type document, status loaded)]
}