ArangoDB v3.10 reached End of Life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
This documentation is outdated. Please see the most recent stable version.
Datacenter-to-Datacenter Replication
A detailed guide to Datacenter-to-Datacenter Replication (DC2DC) for clusters and the arangosync tool
ArangoDB Enterprise Edition
At some point in the grows of a database, there comes a need for replicating it across multiple datacenters.
Reasons for that can be:
- Fallback in case of a disaster in one datacenter
- Regional availability
- Separation of concerns
And many more.
ArangoDB supports Datacenter-to-Datacenter Replication, via the arangosync tool.
ArangoDB’s Datacenter-to-Datacenter Replication is a solution that enables you to asynchronously replicate the entire structure and content in an ArangoDB Cluster in one place to a Cluster in another place. Typically it is used from one datacenter to another. It is possible to replicate to multiple other datacenters as well. It is not a solution for replicating single server instances.
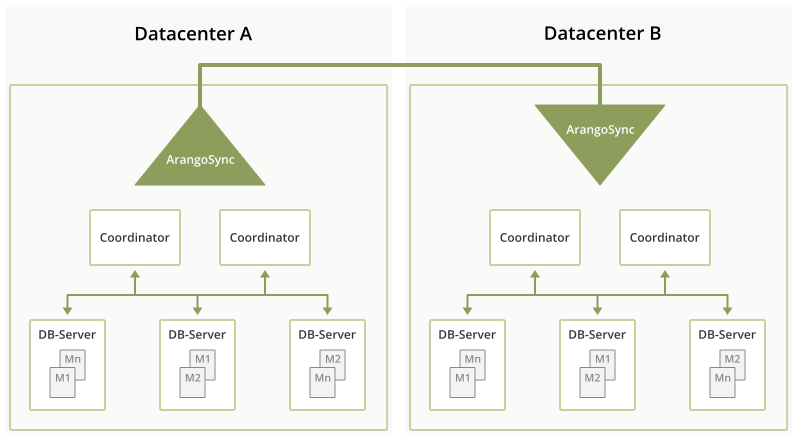
The replication done by ArangoSync is asynchronous. That means that when a client is writing data into the source datacenter, it will consider the request finished before the data has been replicated to the other datacenter. The time needed to completely replicate changes to the other datacenter is typically in the order of seconds, but this can vary significantly depending on load, network & computer capacity.
ArangoSync performs replication in a single direction only. That means that you can replicate data from cluster A to cluster B or from cluster B to cluster A, but never at the same time (one leader, one or more follower clusters). Data modified in the destination cluster will be lost!
Replication is a completely autonomous process. Once it is configured it is designed to run 24/7 without frequent manual intervention. This does not mean that it requires no maintenance or attention at all. As with any distributed system some attention is needed to monitor its operation and keep it secure (e.g. certificate & password rotation).
In the event of an outage of the leader cluster, user intervention is required to either bring the leader back up or to decide on making a follower cluster the new leader. There is no automatic failover as follower clusters lag behind the leader because of network latency etc. and resuming operation with the state of a follower cluster can therefore result in the loss of recent writes. How much can be lost largely depends on the data rate of the leader cluster and the delay between the leader and the follower clusters. Followers will typically be behind the leader by a couple of seconds or minutes.
Once configured, ArangoSync will replicate both structure and data of an entire cluster. This means that there is no need to make additional configuration changes when adding/removing databases or collections. Also meta data such as users, Foxx application & jobs are automatically replicated.
A message queue developed by ArangoDB in Go and called DirectMQ is used for replication. It is tailored for DC2DC replication with efficient native networking routines.
When to use it… and when not
The Datacenter-to-Datacenter Replication is a good solution in all cases where you want to replicate data from one cluster to another without the requirement that the data is available immediately in the other cluster.
The Datacenter-to-Datacenter Replication is not a good solution when one of the following applies:
- You want to replicate data from cluster A to cluster B and from cluster B to cluster A at the same time.
- You need synchronous replication between 2 clusters.
- There is no network connection between cluster A and B.
- You want complete control over which database, collection & documents are replicate and which not.
Requirements
To use Datacenter-to-Datacenter Replication you need the following:
- Two datacenters, each running an ArangoDB Enterprise Edition cluster.
- A network connection between both datacenters with accessible endpoints for several components (see individual components for details).
- TLS certificates for ArangoSync master instances (can be self-signed).
- Optional (but recommended) TLS certificates for ArangoDB clusters (can be self-signed).
- Client certificates CA for ArangoSync masters (typically self-signed).
- Client certificates for ArangoSync masters (typically self-signed).
- At least 2 instances of the ArangoSync master in each datacenter.
- One instances of the ArangoSync worker on every machine in each datacenter.
Besides the above list, you probably want to use the following:
- An orchestrator to keep all components running, e.g.
systemd. - A log file collector for centralized collection & access to the logs of all components.
- A metrics collector & viewing solution such as Prometheus + Grafana.
Limitations
The Datacenter-to-Datacenter Replication setup in ArangoDB has a few limitations. Some of these limitations may be removed in later versions of ArangoDB:
All the machines where the ArangoDB Server processes run must run the Linux operating system using the AMD64 (x86-64) or ARM64 (AArch64) architecture. Clients can run from any platform.
All the machines where the ArangoSync Server processes run must run the Linux operating system using the AMD64 (x86-64) or ARM64 (AArch64) architecture. The ArangoSync command line tool is available for Linux, Windows & macOS.
The entire cluster is replicated. It is not possible to exclude specific databases or collections from replication.
In any DC2DC setup, the minor version of the target cluster must be equal to or greater than the minor version of the source cluster. Replication from a higher to a lower minor version (i.e., from 3.9.x to 3.8.x) is not supported. Syncing between different patch versions of the same minor version is possible, however. For example, you cannot sync from a 3.9.1 cluster to a 3.8.7 cluster, but you can sync from a 3.9.1 cluster to a 3.9.0 cluster.
