Private endpoint deployments in ArangoGraph
Use the private endpoint feature to isolate your deployments and increase security
This topic describes how to create a private endpoint deployment and securely deploy to various cloud providers such as Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and Amazon Web Services (AWS). Follow the steps outlined below to get started.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers a feature called Private Service Connect that allows private consumption of services across VPC networks that belong to different groups, teams, projects, or organizations. You can publish and consume services using the defined IP addresses which are internal to your VPC network.
In ArangoGraph, you can create a regular deployment and change it to a private endpoint deployment afterwards.
Such a deployment is not reachable from the internet anymore, other than via the ArangoGraph dashboard to administrate it. To revert to a public deployment, please contact support via Request help in the help menu.
To configure a private endpoint for GCP, you need to provide your Google project names. ArangoGraph then configures a Private Endpoint Service that automatically connect to private endpoints that are created for those projects.
After the creation of the Private Endpoint Service, you should receive a service attachment that you need during the creation of your private endpoint(s).
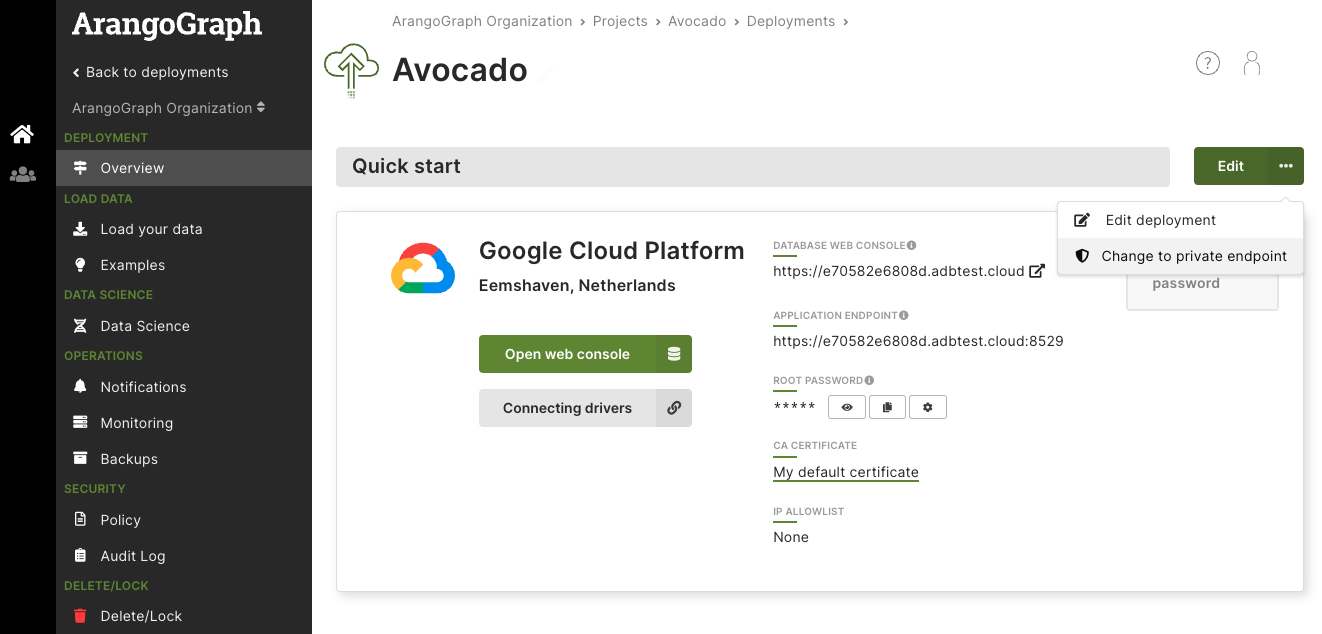
- Open the deployment you want to change.
- In the Quick start section, click the Edit button with an ellipsis (
…) icon. - Click Change to private endpoint in the menu.
- In the configuration wizard, click Next to enter your configuration details.
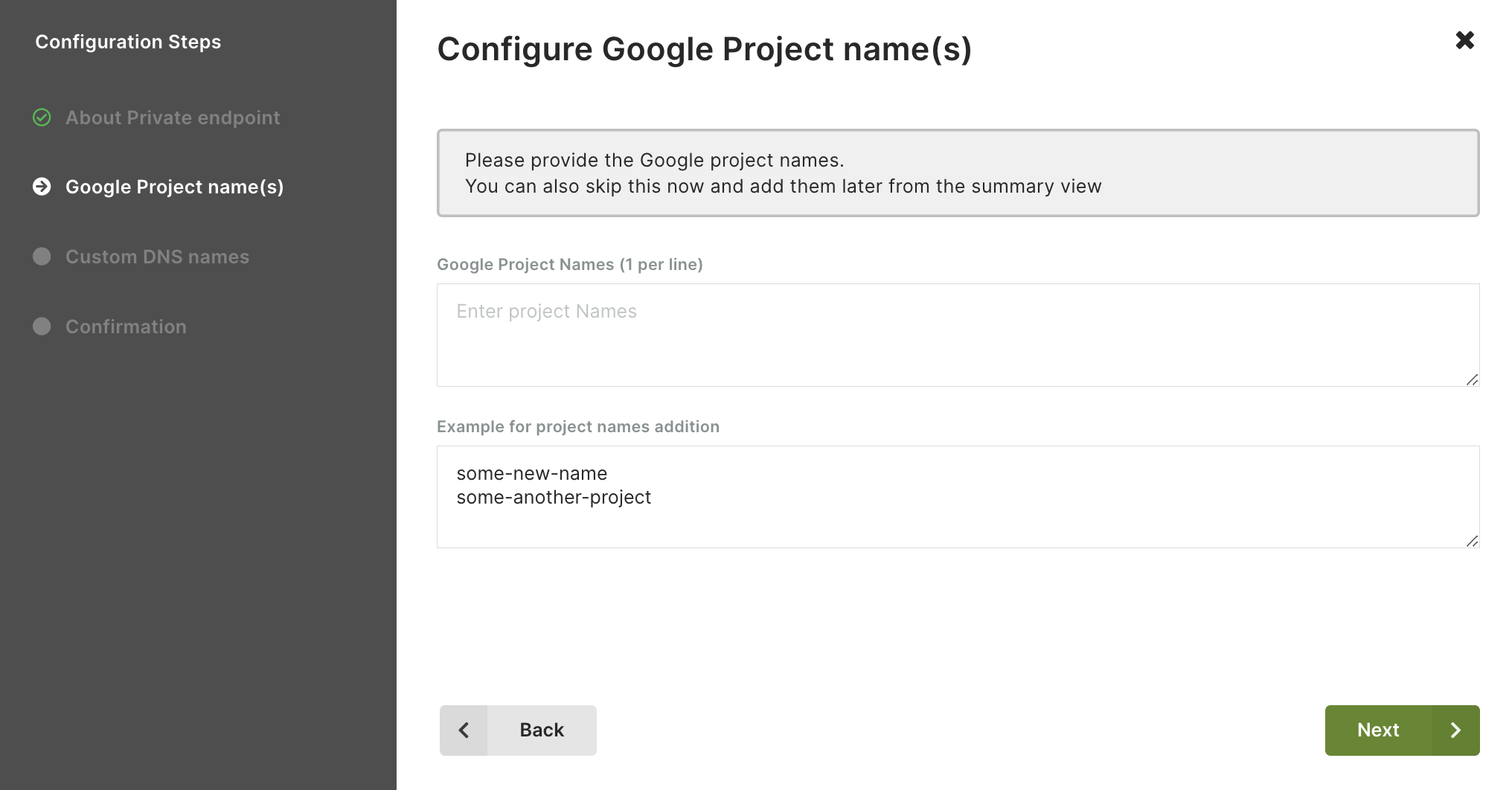
- Enter one or more Google project names. You can also add them later in the summary view.
Click Next.
- Configure custom DNS names. This step is optional and disabled by default.
Note that, once enabled, this setting is immutable and cannot be reverted.
Click Next to continue.By default, your private endpoint is available to all VPCs that connect to it at
https://<endpoint_id>-pe.arangodb.cloudwith the well-known certificate. If the custom DNS is enabled, you will be responsible for the DNS of your private endpoints.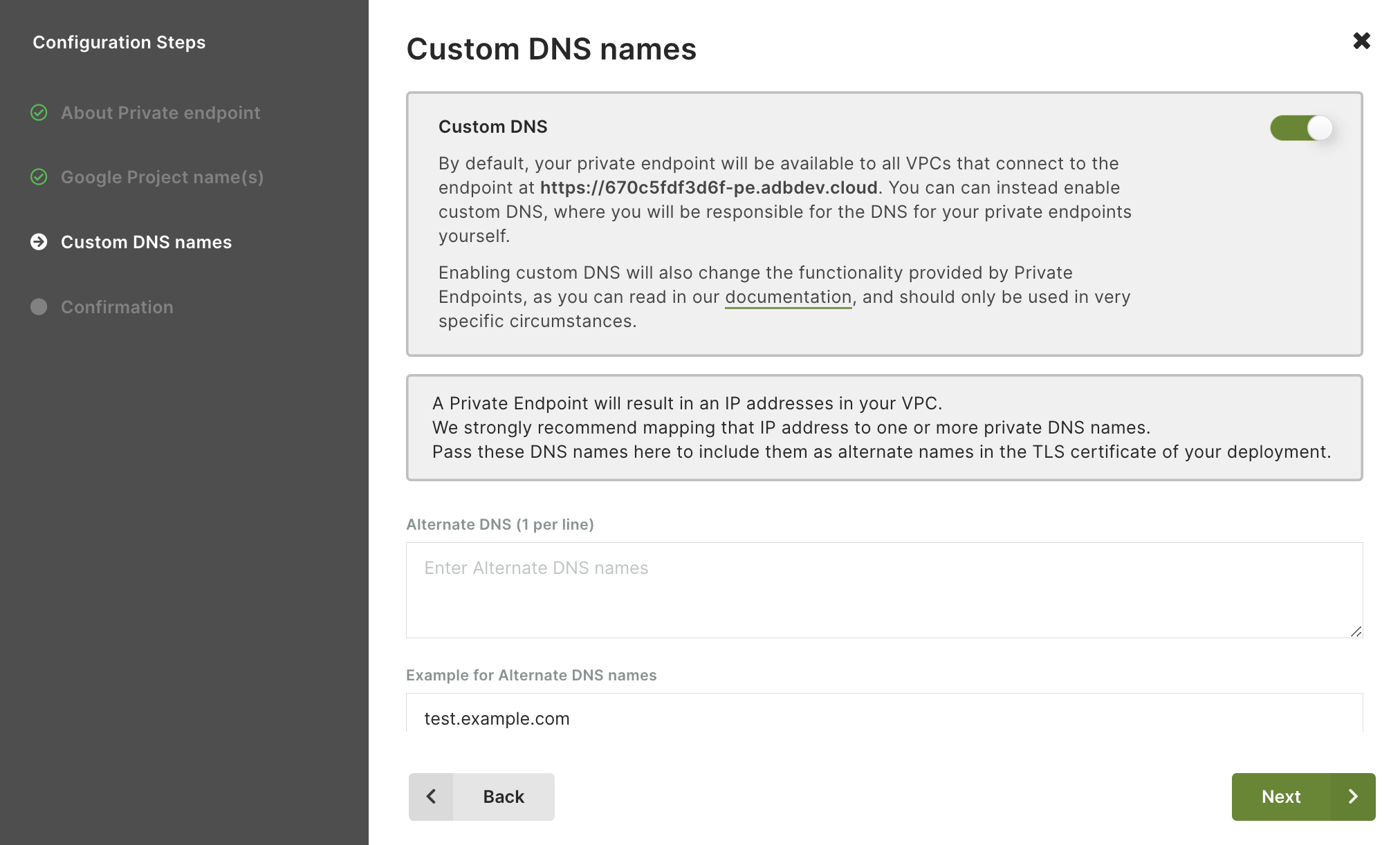
- Click Confirm Settings to change the deployment.
- Back in the Overview page, scroll down to the Private Endpoint section that is now displayed to see the connection status and to change the configuration.
- ArangoGraph configures a Private Endpoint Service. As soon as the Service Attachment is ready, you can use it to configure the Private Service Connect in your VPC.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS offers a feature called AWS PrivateLink that enables you to privately connect your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to services, without exposure to the internet. You can control the specific API endpoints, sites, and services that are reachable from your VPC.
Amazon VPC allows you to launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you have defined. It closely resembles a traditional network that you would normally operate, with the benefits of using the AWS scalable infrastructure.
In ArangoGraph, you can create a regular deployment and change it to a private endpoint deployment afterwards.
The ArangoDB private endpoint deployment is not exposed to public internet anymore, other than via the ArangoGraph dashboard to administrate it. To revert it to a public deployment, please contact the support team via Request help in the help menu.
To configure a private endpoint for AWS, you need to provide the AWS principals related to your VPC. The ArangoGraph Insights Platform configures a Private Endpoint Service that automatically connects to private endpoints that are created in those principals.
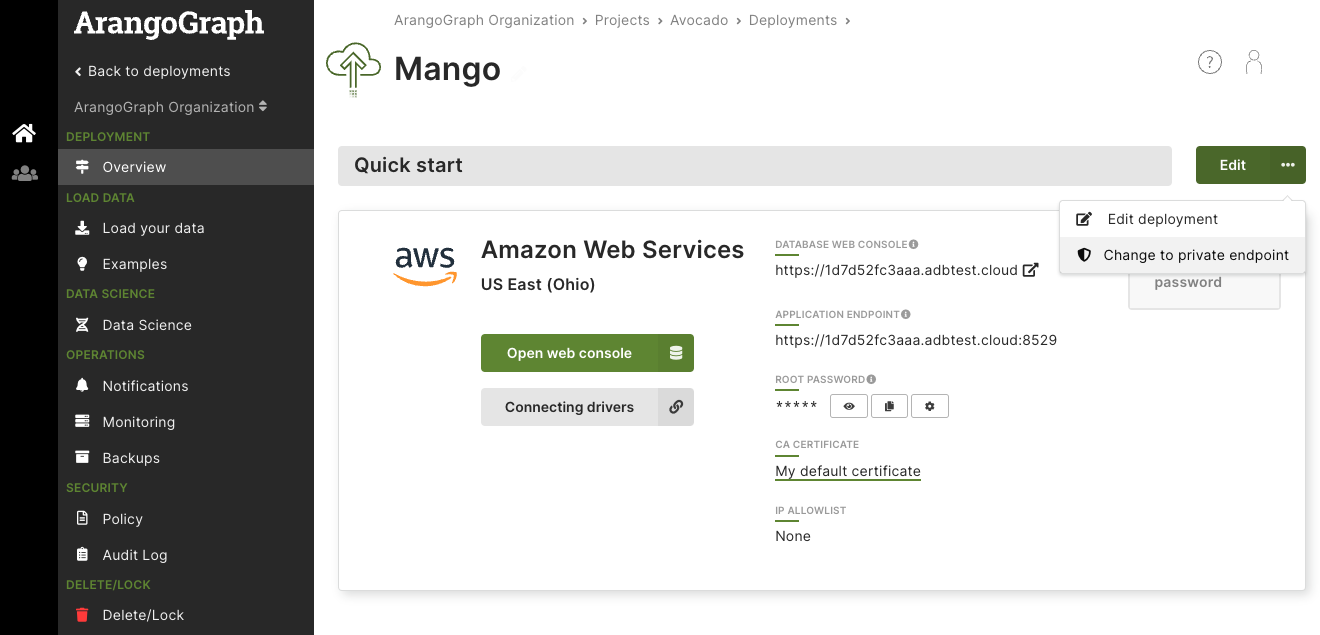
Open the deployment you want to change.
In the Quick start section, click the Edit button with an ellipsis (
…) icon.Click Change to private endpoint in the menu.
In the configuration wizard, click Next to enter your configuration details.
Click Add Principal to start configuring the AWS principal(s). You need to enter a valid account, which is your 12 digit AWS account ID. Adding usernames or role names is optional. You can also skip this step and add them later from the summary view.
Principals cannot be changed anymore once a connection has been established.To verify your endpoint service in AWS, you must use the same principal as configured in ArangoGraph. Otherwise, the service name cannot be verified.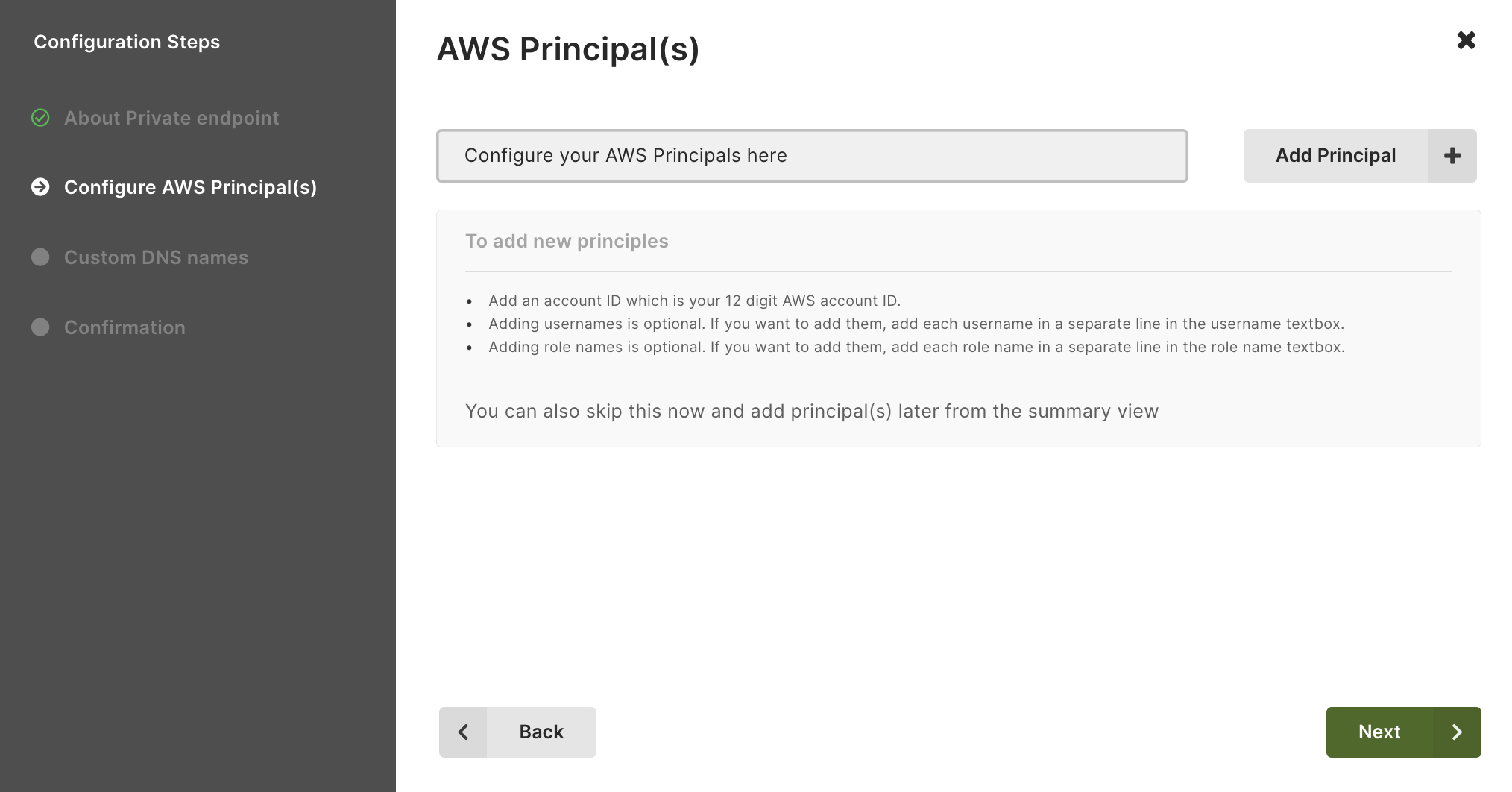
Configure custom DNS names. This step is optional and disabled by default, you can also add or change them later from the summary view. Click Next to continue.
By default, your private endpoint is available to all VPCs that connect to it athttps://<endpoint_id>-pe.arangodb.cloudwith the well-known certificate. If the custom DNS is enabled, you will be responsible for the DNS of your private endpoints.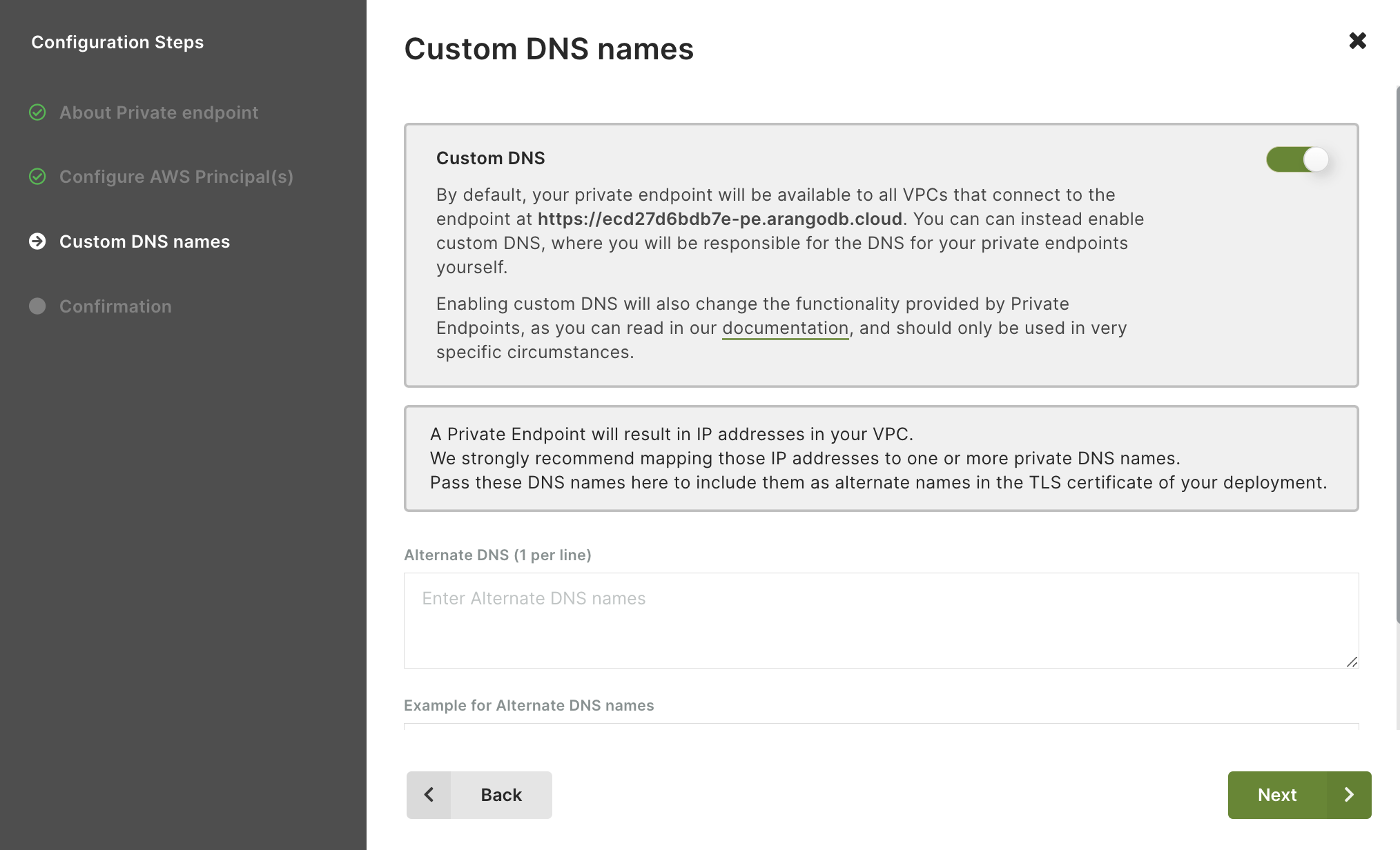
Confirm that you want to use a private endpoint for your deployment by clicking Confirm Settings.
Back in the Overview page, scroll down to the Private Endpoint section that is now displayed to see the connection status and change the configuration, if needed.
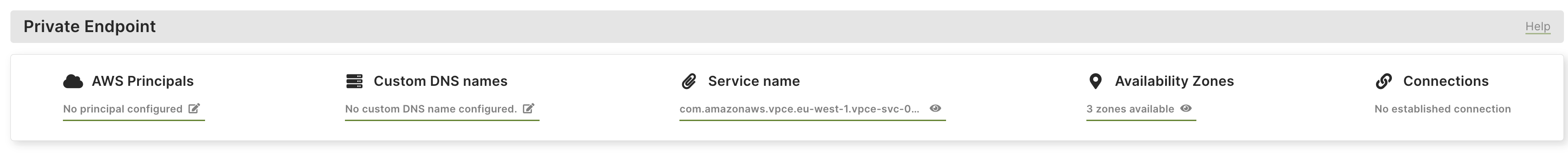 Note that Availability Zones are independently mapped for each AWS account. The physical location of a zone may differ from one account to another account. To coordinate Availability Zones across AWS accounts, you must use the Availability Zone ID .To learn more or request help from the ArangoGraph support team, click Help in the top right corner of the Private Endpoint section.
Note that Availability Zones are independently mapped for each AWS account. The physical location of a zone may differ from one account to another account. To coordinate Availability Zones across AWS accounts, you must use the Availability Zone ID .To learn more or request help from the ArangoGraph support team, click Help in the top right corner of the Private Endpoint section.ArangoGraph configures a Private Endpoint Service. As soon as this is available, you can use it in the AWS portal to create an interface endpoint to connect to your endpoint service. For more details, see How to connect to an endpoint .
