ArangoDB v3.13 is under development and not released yet. This documentation is not final and potentially incomplete.
Shortest Path in AQL
Find one path of shortest length between two nodes
General query idea
This type of query finds the shortest path between two given documents (startNode and endNode) in your graph. If there are multiple shortest paths, the path with the lowest weight or a random one (in case of a tie) is returned.
The shortest path search emits the following two variables for every step of the path:
- The node on this path.
- The edge pointing to it.
Example execution
Let’s take a look at a simple example to explain how it works. This is the graph that you are going to find a shortest path on:
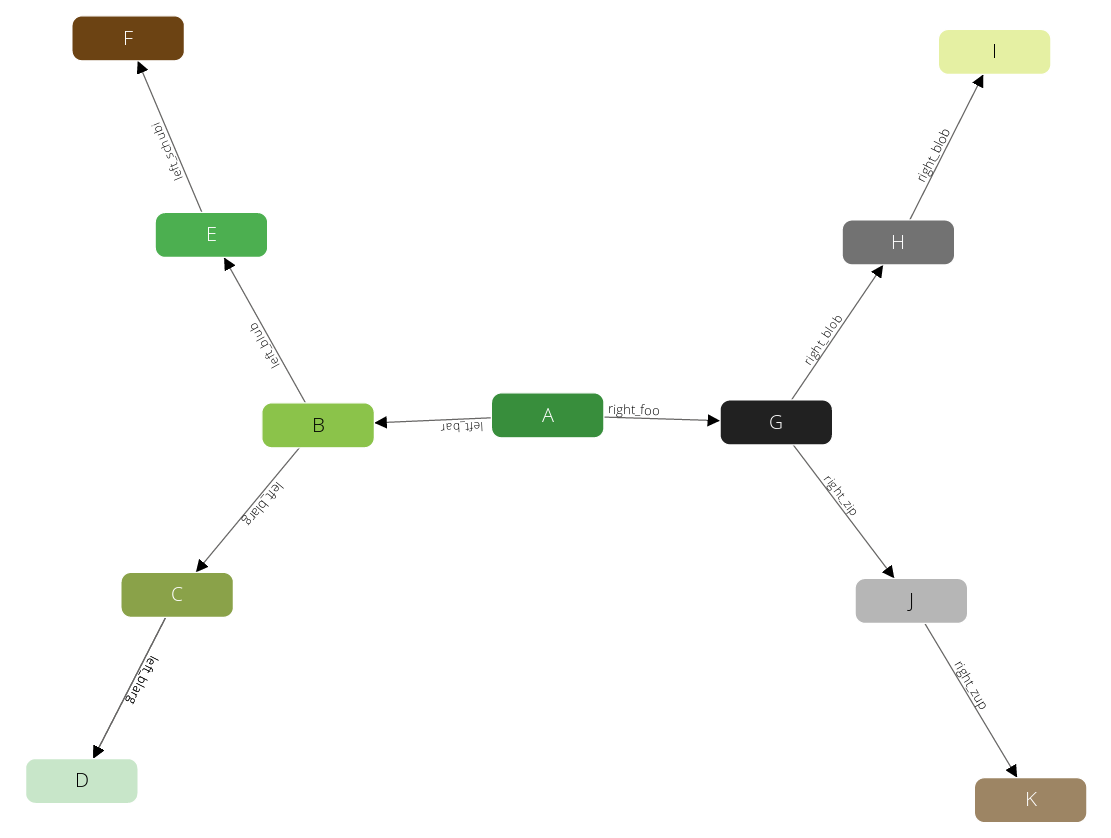
You can use the following parameters for the query:
- You start at the node A.
- You finish with the node D.
So, obviously, you have the nodes A, B, C and D on the shortest path in exactly this order. Then, the shortest path statement returns the following pairs:
| Node | Edge |
|---|---|
| A | null |
| B | A → B |
| C | B → C |
| D | C → D |
Note that the first edge is always null because there is no edge pointing
to the startNode.
Syntax
The next step is to see how you can write a shortest path query. You have two options here, you can either use a named graph or a set of edge collections (anonymous graph).
Working with named graphs
FOR node[, edge]
IN OUTBOUND|INBOUND|ANY SHORTEST_PATH
startNode TO endNode
GRAPH graphName
[OPTIONS options]FOR: Emits up to two variables:- node (object): The current node on the shortest path
- edge (object, optional): The edge pointing to the node
INOUTBOUND|INBOUND|ANY: Defines in which direction edges are followed (outgoing, incoming, or both)- startNode
TOendNode (both string|object): The two nodes between which the shortest path is computed. This can be specified in the form of an ID string or in the form of a document with the attribute_id. All other values lead to a warning and an empty result. If one of the specified documents does not exist, the result is empty as well and there is no warning. GRAPHgraphName (string): The name identifying the named graph. Its node and edge collections are looked up for the path search.OPTIONSoptions (object, optional): See the path search options.
weightAttribute) with a negative value is
encountered during traversal, or if defaultWeight is set to a negative
number, then the query is aborted with an error.Working with collection sets
FOR node[, edge]
IN OUTBOUND|INBOUND|ANY SHORTEST_PATH
startNode TO endNode
edgeCollection1, ..., edgeCollectionN
[OPTIONS options]Instead of GRAPH graphName you may specify a list of edge collections (anonymous
graph). The involved node collections are determined by the edges of the given
edge collections. The rest of the behavior is similar to the named version.
Path search options
You can optionally specify the following options to modify the execution of a graph path search. If you specify unknown options, query warnings are raised.
weightAttribute
A top-level edge attribute that should be used to read the edge weight (string).
If the attribute does not exist or is not numeric, the defaultWeight is used
instead.
The attribute value must not be negative.
defaultWeight
This value is used as fallback if there is no weightAttribute in the
edge document, or if it’s not a number (number).
The value must not be negative. The default is 1.
useCache
Introduced in: v3.12.2
Whether to use the in-memory cache for edges. The default is true.
You can set this option to false to not make a large graph operation pollute
the edge cache.
Traversing in mixed directions
For shortest path with a list of edge collections you can optionally specify the
direction for some of the edge collections. Say for example you have three edge
collections edges1, edges2 and edges3, where in edges2 the direction
has no relevance, but in edges1 and edges3 the direction should be taken into
account. In this case you can use OUTBOUND as general search direction and ANY
specifically for edges2 as follows:
FOR node IN OUTBOUND SHORTEST_PATH
startNode TO endNode
edges1, ANY edges2, edges3All collections in the list that do not specify their own direction use the
direction defined after IN (here: OUTBOUND). This allows you to use a different
direction for each collection in your path search.
Graph path searches in a cluster
Due to the nature of graphs, edges may reference nodes from arbitrary collections. Following the paths can thus involve documents from various collections and it is not possible to predict which are visited in a path search - unless you use named graphs that define all node and edge collections that belong to them and the graph data is consistent.
If you use anonymous graphs / collection sets for graph queries, which node collections need to be loaded by the graph engine can deduced automatically if there is a named graph with a matching edge collection in its edge definitions (introduced in v3.12.6). Edge collections are always declared explicitly in queries, directly or via referencing a named graph.
Without a named graph, the involved node collections can only be determined at
run time. Use the WITH operation to
declare the node collections upfront. This is required for path searches
using collection sets in cluster deployments (if there is no named graph to
deduce the node collections from). Declare the collection of the start node as
well if it’s not declared already (like by a FOR loop).
For example, suppose you have two node collections, person and movie, and
an acts_in edge collection that connects them. If you want to run a path search
query that starts (and ends) at a person that you specify with its document ID,
you need to declare both node collections at the beginning of the query:
WITH person, movie
FOR v IN ANY SHORTEST_PATH "person/1544" TO "person/52560" acts_in
RETURN v.labelHowever, if there is a named graph that includes an edge definition for the
acts_in edge collection, with person as the from collection and movie
as the to collection, you can omit WITH person, movie. That is, if you
specify acts_in as an edge collection in an anonymous graph query, all
named graphs are checked for this edge collection, and if there is a matching
edge definition, its node collections are automatically added as data sources to
the query.
FOR v IN ANY SHORTEST_PATH "person/1544" TO "person/52560" acts_in
RETURN v.label
// Chris Rock --> Dogma <-- Ben Affleck --> Surviving Christmas <-- Jennifer Morrison
You can still declare collections manually, in which case they are added as data sources in addition to automatically deduced collections.
Conditional shortest path
The SHORTEST_PATH computation only finds an unconditioned shortest path.
With this construct it is not possible to define a condition like: “Find the
shortest path where all edges are of type X”. If you want to do this, use a
normal Traversal instead with the option
{order: "bfs"} in combination with LIMIT 1.
Please also consider using WITH to specify the
collections you expect to be involved.
Examples
Creating a simple symmetric traversal demonstration graph:

var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
var graph = examples.loadGraph("traversalGraph");
db.circles.toArray();
db.edges.toArray();Show output
[
{
"_key" : "A",
"_id" : "circles/A",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkG---",
"label" : "1"
},
{
"_key" : "B",
"_id" : "circles/B",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkG--_",
"label" : "2"
},
{
"_key" : "C",
"_id" : "circles/C",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkG--A",
"label" : "3"
},
{
"_key" : "D",
"_id" : "circles/D",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkG--B",
"label" : "4"
},
{
"_key" : "E",
"_id" : "circles/E",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkG--C",
"label" : "5"
},
{
"_key" : "F",
"_id" : "circles/F",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkG--D",
"label" : "6"
},
{
"_key" : "G",
"_id" : "circles/G",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkK---",
"label" : "7"
},
{
"_key" : "H",
"_id" : "circles/H",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkK--_",
"label" : "8"
},
{
"_key" : "I",
"_id" : "circles/I",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkK--A",
"label" : "9"
},
{
"_key" : "J",
"_id" : "circles/J",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkK--B",
"label" : "10"
},
{
"_key" : "K",
"_id" : "circles/K",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkK--C",
"label" : "11"
}
]
[
{
"_key" : "63945",
"_id" : "edges/63945",
"_from" : "circles/A",
"_to" : "circles/B",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkK--D",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_bar"
},
{
"_key" : "63947",
"_id" : "edges/63947",
"_from" : "circles/B",
"_to" : "circles/C",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkO---",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_blarg"
},
{
"_key" : "63949",
"_id" : "edges/63949",
"_from" : "circles/C",
"_to" : "circles/D",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkO--_",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_blorg"
},
{
"_key" : "63951",
"_id" : "edges/63951",
"_from" : "circles/B",
"_to" : "circles/E",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkO--A",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_blub"
},
{
"_key" : "63953",
"_id" : "edges/63953",
"_from" : "circles/E",
"_to" : "circles/F",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkO--B",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "left_schubi"
},
{
"_key" : "63955",
"_id" : "edges/63955",
"_from" : "circles/A",
"_to" : "circles/G",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkO--C",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_foo"
},
{
"_key" : "63957",
"_id" : "edges/63957",
"_from" : "circles/G",
"_to" : "circles/H",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkO--D",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_blob"
},
{
"_key" : "63959",
"_id" : "edges/63959",
"_from" : "circles/H",
"_to" : "circles/I",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkO--E",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_blub"
},
{
"_key" : "63961",
"_id" : "edges/63961",
"_from" : "circles/G",
"_to" : "circles/J",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkS---",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_zip"
},
{
"_key" : "63963",
"_id" : "edges/63963",
"_from" : "circles/J",
"_to" : "circles/K",
"_rev" : "_hg5kIkS--_",
"theFalse" : false,
"theTruth" : true,
"label" : "right_zup"
}
]Start with the shortest path from A to D as above:
db._query(`
FOR v, e IN OUTBOUND SHORTEST_PATH 'circles/A' TO 'circles/D' GRAPH 'traversalGraph'
RETURN [v._key, e._key]
`);
db._query(`
FOR v, e IN OUTBOUND SHORTEST_PATH 'circles/A' TO 'circles/D' edges
RETURN [v._key, e._key]
`);Show output
[object ArangoQueryCursor, count: 4, cached: false, hasMore: false]
[
[
"A",
null
],
[
"B",
"63945"
],
[
"C",
"63947"
],
[
"D",
"63949"
]
]
[object ArangoQueryCursor, count: 4, cached: false, hasMore: false]
[
[
"A",
null
],
[
"B",
"63945"
],
[
"C",
"63947"
],
[
"D",
"63949"
]
]You can see that expectations are fulfilled. You find the nodes in the
correct ordering and the first edge is null, because no edge is pointing
to the start node on this path.
You can also compute shortest paths based on documents found in collections:
db._query(`
FOR a IN circles
FILTER a._key == 'A'
FOR d IN circles
FILTER d._key == 'D'
FOR v, e IN OUTBOUND SHORTEST_PATH a TO d GRAPH 'traversalGraph'
RETURN [v._key, e._key]
`);
db._query(`
FOR a IN circles
FILTER a._key == 'A'
FOR d IN circles
FILTER d._key == 'D'
FOR v, e IN OUTBOUND SHORTEST_PATH a TO d edges
RETURN [v._key, e._key]
`);Show output
[object ArangoQueryCursor, count: 4, cached: false, hasMore: false]
[
[
"A",
null
],
[
"B",
"63945"
],
[
"C",
"63947"
],
[
"D",
"63949"
]
]
[object ArangoQueryCursor, count: 4, cached: false, hasMore: false]
[
[
"A",
null
],
[
"B",
"63945"
],
[
"C",
"63947"
],
[
"D",
"63949"
]
]And finally clean it up again:
var examples = require("@arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph");
examples.dropGraph("traversalGraph");Show output
Empty Output